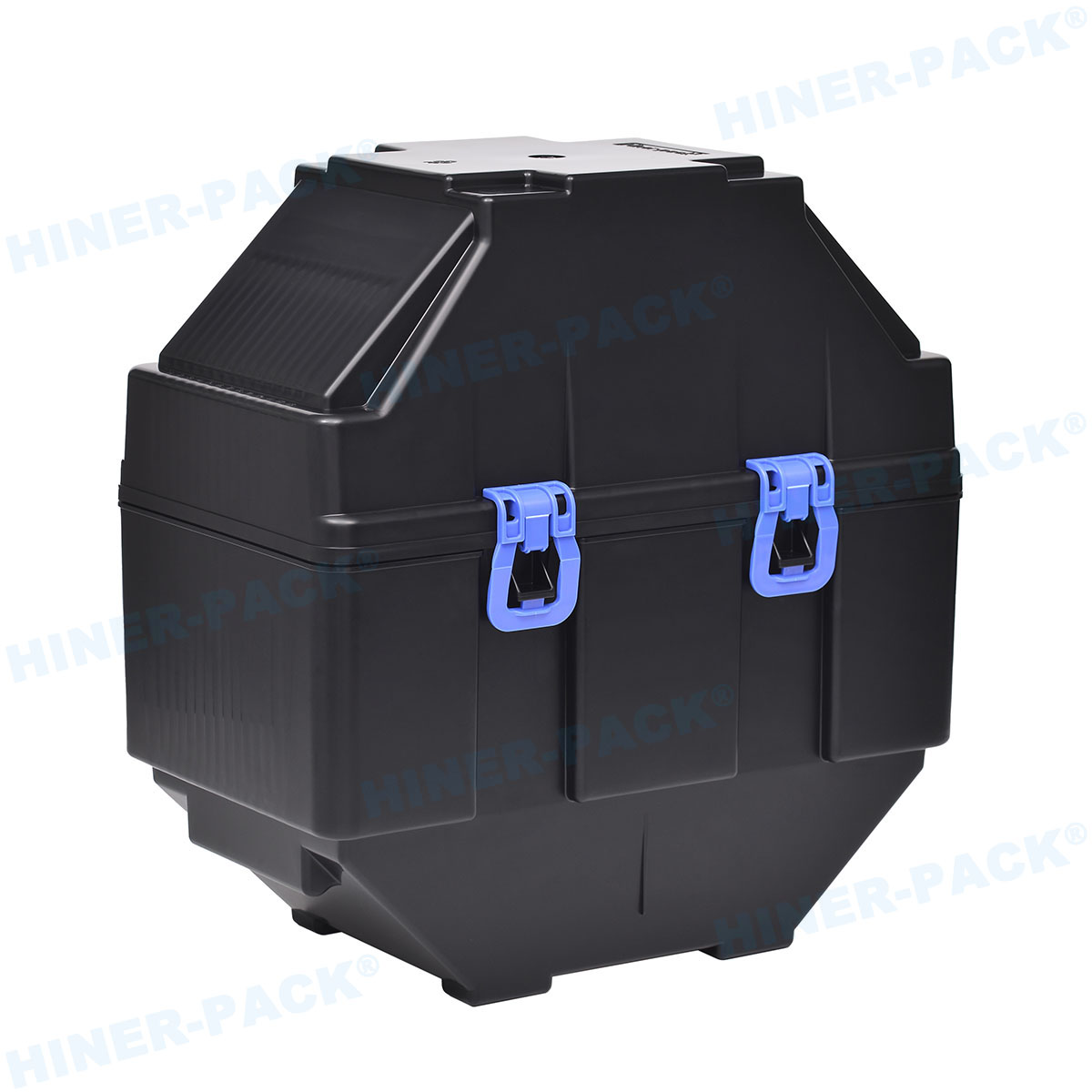
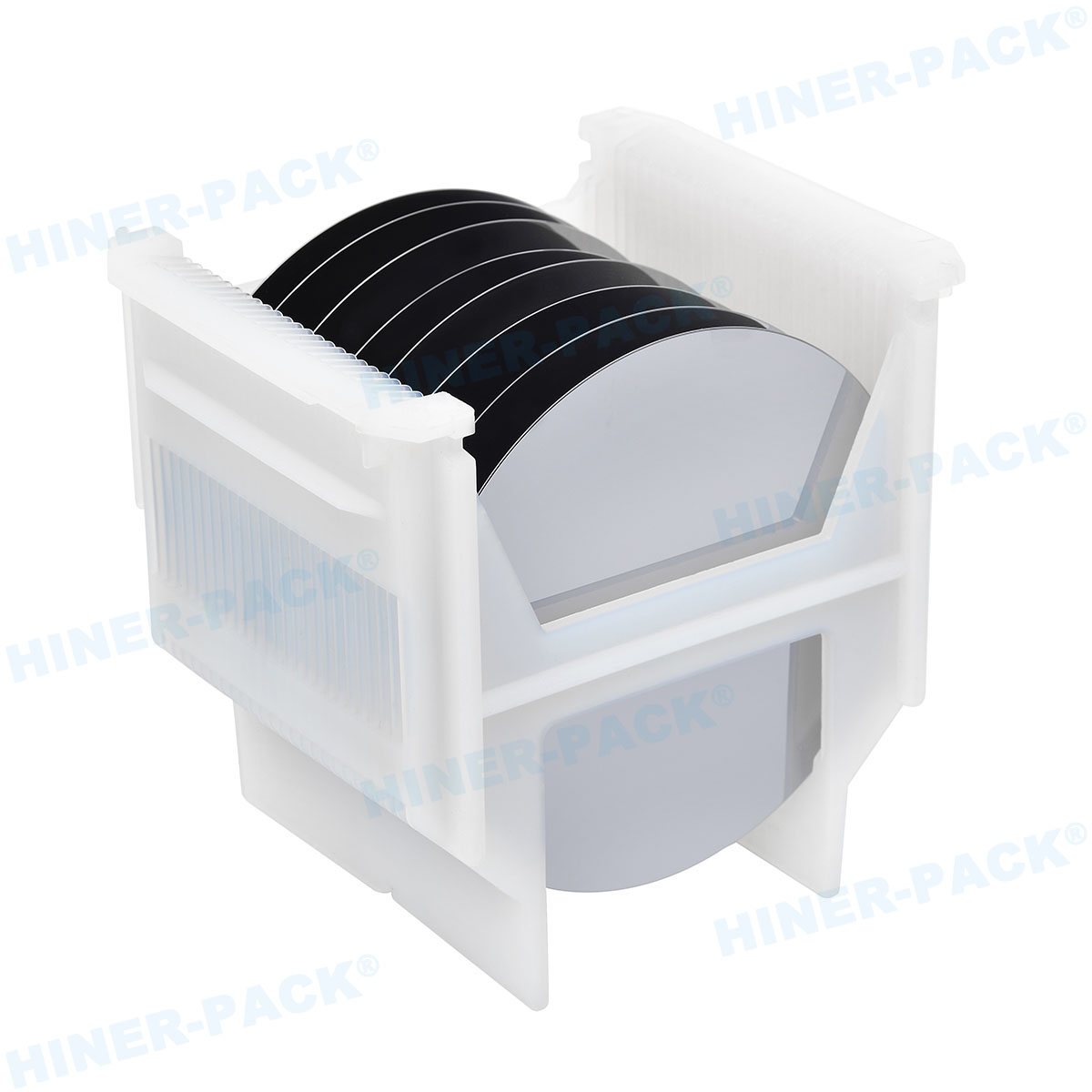
In the highly precise world of semiconductor manufacturing, every component plays a critical role in ensuring product quality and yield. Among these, the Teflon wafer carrier stands out as a vital tool for handling silicon wafers during processes like etching, cleaning, and chemical treatments. Made from polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), commonly known by the brand name Teflon, these carriers are designed to minimize contamination and withstand harsh environments. This article delves into the key aspects of Teflon wafer carriers, highlighting their benefits and applications in modern technology. By understanding their importance, manufacturers can make informed decisions to optimize their production lines. Whether you're involved in chip fabrication or research, learning about Teflon wafer carriers can lead to improved operational efficiency and reduced defects.

What is a Teflon Wafer Carrier?
A Teflon wafer carrier is a specialized container or holder used in the semiconductor industry to transport and process silicon wafers. These wafers, which form the base for electronic circuits, require extreme care to avoid damage from contaminants, static, or physical stress. Teflon, a material renowned for its non-stick and inert properties, makes these carriers ideal for applications involving aggressive chemicals and high temperatures. Typically, a Teflon wafer carrier features slots or grooves that securely hold wafers in place, preventing movement during handling or processing. This design ensures that the wafers remain pristine, reducing the risk of scratches or particle adhesion. As semiconductor nodes shrink to nanometer scales, the role of Teflon wafer carriers becomes even more crucial in maintaining wafer integrity. Industries rely on these carriers for consistent performance in cleanrooms and fabrication facilities.
Superior Chemical Resistance of Teflon Wafer Carriers
One of the primary reasons Teflon wafer carriers are favored in semiconductor processes is their exceptional chemical resistance. Silicon wafer manufacturing often involves exposure to corrosive substances like acids, bases, and solvents during cleaning, etching, or deposition stages. Teflon, being a fluoropolymer, is virtually impervious to most chemicals, ensuring that the carrier does not degrade or leach impurities into the process environment. This resistance helps maintain the purity of the wafers, preventing defects that could lead to device failure. For instance, in wet bench operations, a Teflon wafer carrier can withstand prolonged contact with hydrofluoric acid or sulfuric acid without swelling or cracking. This durability translates to longer service life and reduced replacement costs, making Teflon wafer carriers a cost-effective solution for high-volume production. Compared to carriers made from metals or other plastics, Teflon variants offer a safer and more reliable option, minimizing the risk of chemical-induced contamination.
High-Temperature Stability in Demanding Environments
Semiconductor fabrication often involves extreme temperatures, from ambient conditions to over 200°C in processes like thermal oxidation or annealing. Teflon wafer carriers excel in such environments due to their high thermal stability. PTFE can continuously operate at temperatures up to 260°C without melting or deforming, ensuring that the carriers maintain their structural integrity under heat stress. This property is essential for preventing wafer warping or misalignment during high-temperature steps. Additionally, Teflon wafer carriers exhibit low thermal expansion, meaning they do not significantly change size with temperature fluctuations. This consistency helps in maintaining precise wafer positioning, which is critical for lithography and other alignment-sensitive operations. In applications like plasma etching or chemical vapor deposition, where temperature spikes are common, using a Teflon wafer carrier reduces the likelihood of process variations. This reliability supports higher yields and consistent product quality, making Teflon an indispensable material for advanced semiconductor nodes.
Low Contamination and Particle Generation
In semiconductor manufacturing, even microscopic particles can cause catastrophic defects in microchips, leading to reduced yields and increased costs. Teflon wafer carriers are designed to minimize contamination risks through their inherent non-porous and non-shedding surfaces. Unlike materials that may release particles or outgas under stress, Teflon remains stable, reducing the introduction of foreign matter into the cleanroom. The smooth surface of a Teflon wafer carrier also prevents wafer sticking, which can occur with other materials, further lowering the chance of particle generation during wafer insertion or removal. This is particularly important in front-end-of-line (FEOL) processes, where wafer surfaces must remain ultraclean. Regular use of Teflon wafer carriers in chemical mechanical polishing (CMP) or diffusion steps ensures that wafers are not exposed to additional contaminants. By adhering to strict industry standards, such as those from SEMI, Teflon wafer carriers help facilities meet contamination control targets, ultimately enhancing overall device reliability and performance.
Durability and Long-Term Cost Efficiency
Investing in Teflon wafer carriers can lead to significant long-term savings due to their durability and low maintenance requirements. These carriers are resistant to wear, corrosion, and mechanical stress, allowing them to withstand repeated use in aggressive industrial settings. For example, a well-maintained Teflon wafer carrier can last for years without significant degradation, unlike carriers made from materials like quartz or stainless steel, which may require frequent replacements or refinishing. This longevity reduces downtime and operational costs associated with carrier procurement and disposal. Moreover, Teflon wafer carriers are easy to clean—often requiring simple rinsing with deionized water or mild solvents—which simplifies maintenance routines and minimizes cross-contamination between batches. In terms of total cost of ownership, the initial higher cost of Teflon wafer carriers is offset by their extended lifespan and reduced defect rates. Companies focusing on sustainable practices also appreciate that Teflon carriers can be recycled or repurposed, aligning with environmental goals while maintaining efficiency.
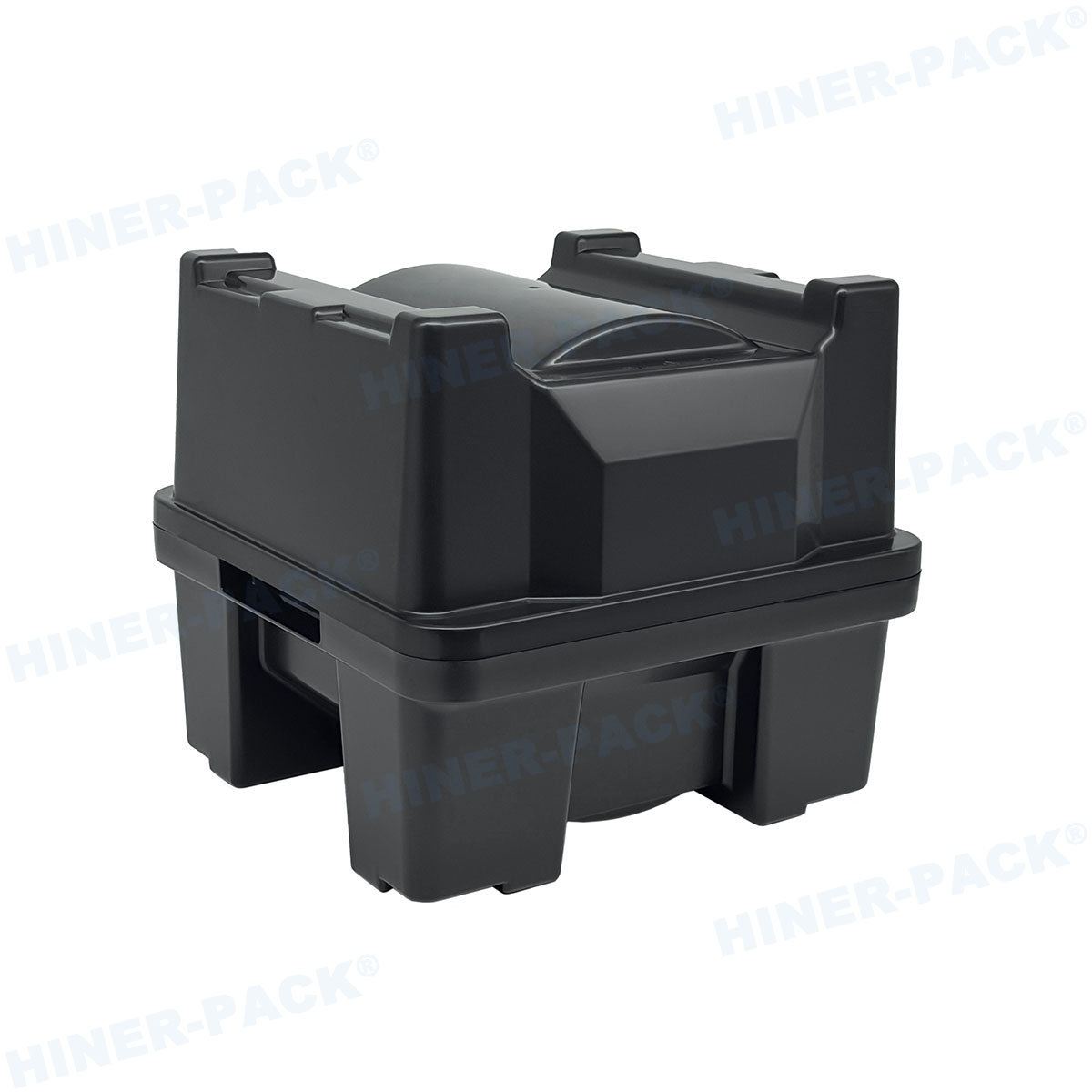

Applications Across Semiconductor and Related Industries
Teflon wafer carriers are not limited to traditional semiconductor fabrication; they find applications in various high-tech fields. In the solar industry, for instance, they are used in the production of photovoltaic cells, where wafers undergo similar chemical and thermal processes. The biomedical sector employs Teflon wafer carriers in the manufacturing of lab-on-a-chip devices and sensors, leveraging their biocompatibility and cleanliness. Additionally, in research and development, these carriers facilitate experiments involving nanomaterials or microelectromechanical systems (MEMS), where precision handling is paramount. The versatility of Teflon wafer carriers extends to emerging technologies like quantum computing and flexible electronics, where wafer integrity is critical. By adapting to diverse requirements, Teflon wafer carriers support innovation across multiple disciplines. Their role in enabling miniaturization and higher integration densities underscores their importance in the ongoing advancement of electronic devices.
Teflon wafer carriers are indispensable components in modern manufacturing, offering a blend of chemical resistance, thermal stability, and contamination control that is hard to match. By incorporating these carriers into semiconductor processes, companies can achieve higher yields, lower costs, and improved product reliability. As technology evolves, the demand for high-performance materials like Teflon will only grow, making it essential for industry professionals to stay informed about their benefits. Whether you're optimizing an existing production line or exploring new applications, Teflon wafer carriers provide a reliable solution for handling sensitive wafers. Embrace the advantages of Teflon wafer carriers to drive efficiency and innovation in your operations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What is a Teflon wafer carrier used for?
A1: A Teflon wafer carrier is primarily used in the semiconductor industry to hold, transport, and process silicon wafers during manufacturing steps such as cleaning, etching, and thermal treatments. Its Teflon construction ensures minimal contamination and resistance to harsh chemicals, making it ideal for maintaining wafer purity in cleanroom environments.
Q2: How does a Teflon wafer carrier compare to one made of quartz?
A2: While quartz wafer carriers offer good thermal stability, Teflon wafer carriers excel in chemical resistance and reduced particle generation. Teflon is less brittle than quartz, reducing breakage risks, and it doesn't require frequent cleaning to prevent contamination. However, quartz may be preferred in very high-temperature applications beyond Teflon's range, but Teflon is generally more versatile for standard processes.
Q3: Can Teflon wafer carriers be customized for specific wafer sizes?
A3: Yes, Teflon wafer carriers can be custom-designed to accommodate various wafer sizes, such as 200mm, 300mm, or even larger diameters. Manufacturers often offer tailored solutions with specific slot configurations, handles, or additional features to fit unique process requirements, ensuring compatibility with different equipment and automation systems.
Q4: What maintenance is required for Teflon wafer carriers?
A4: Maintenance for Teflon wafer carriers typically involves regular cleaning with deionized water or mild solvents to remove residues. They should be inspected for signs of wear or damage, such as cracks or deformation, and stored in a clean, dry environment. Due to Teflon's durability, they require less frequent replacement than other materials, but proper handling avoids scratches that could harbor contaminants.
Q5: Are Teflon wafer carriers environmentally friendly?
A5: Teflon wafer carriers are considered environmentally friendly in terms of longevity and recyclability. PTFE (Teflon) is inert and does not leach harmful substances, but disposal should follow local regulations for plastics. Many facilities recycle Teflon carriers to reduce waste, and their long service life minimizes the environmental impact compared to single-use alternatives. However, production of PTFE involves fluorochemicals, so sourcing from responsible manufacturers is recommended.