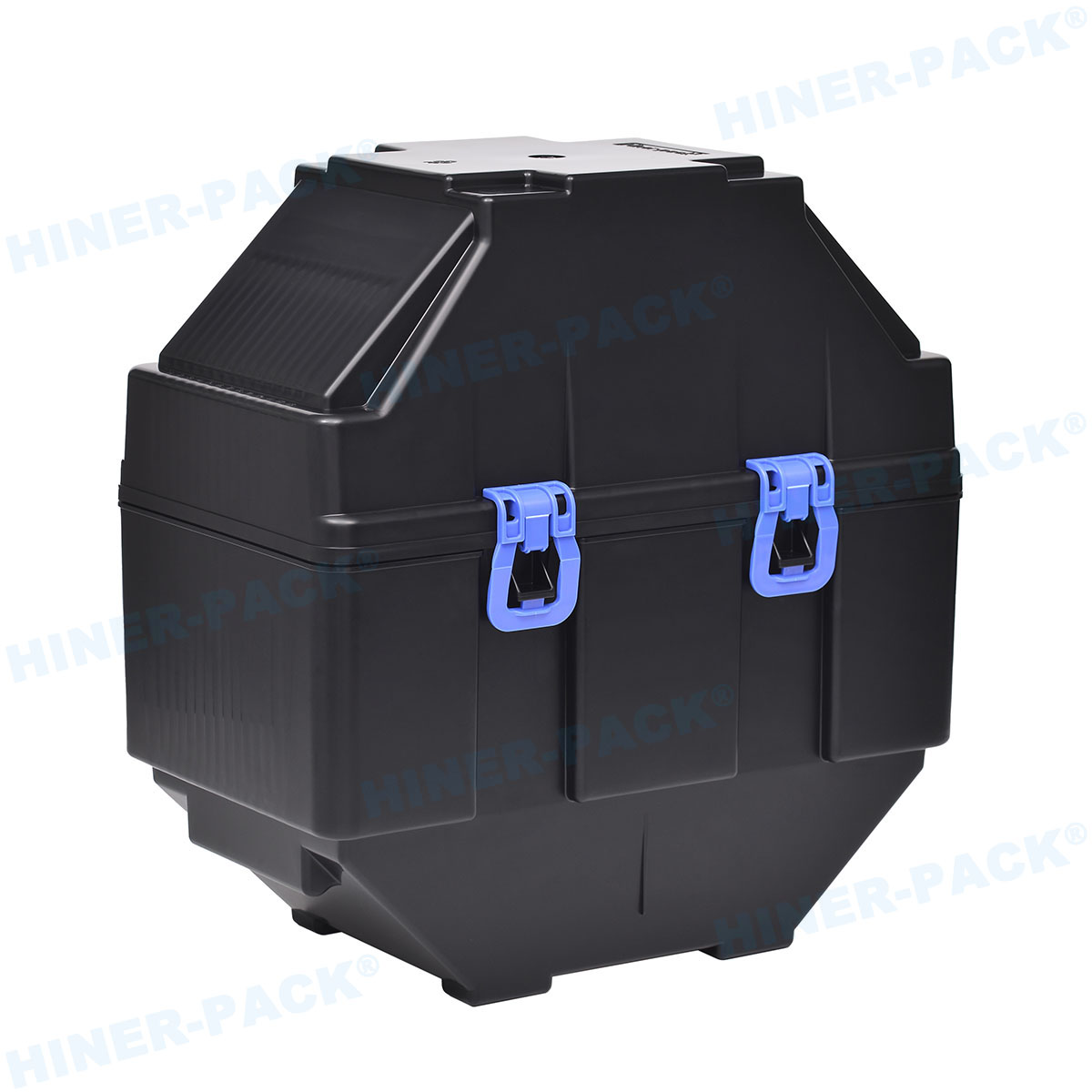
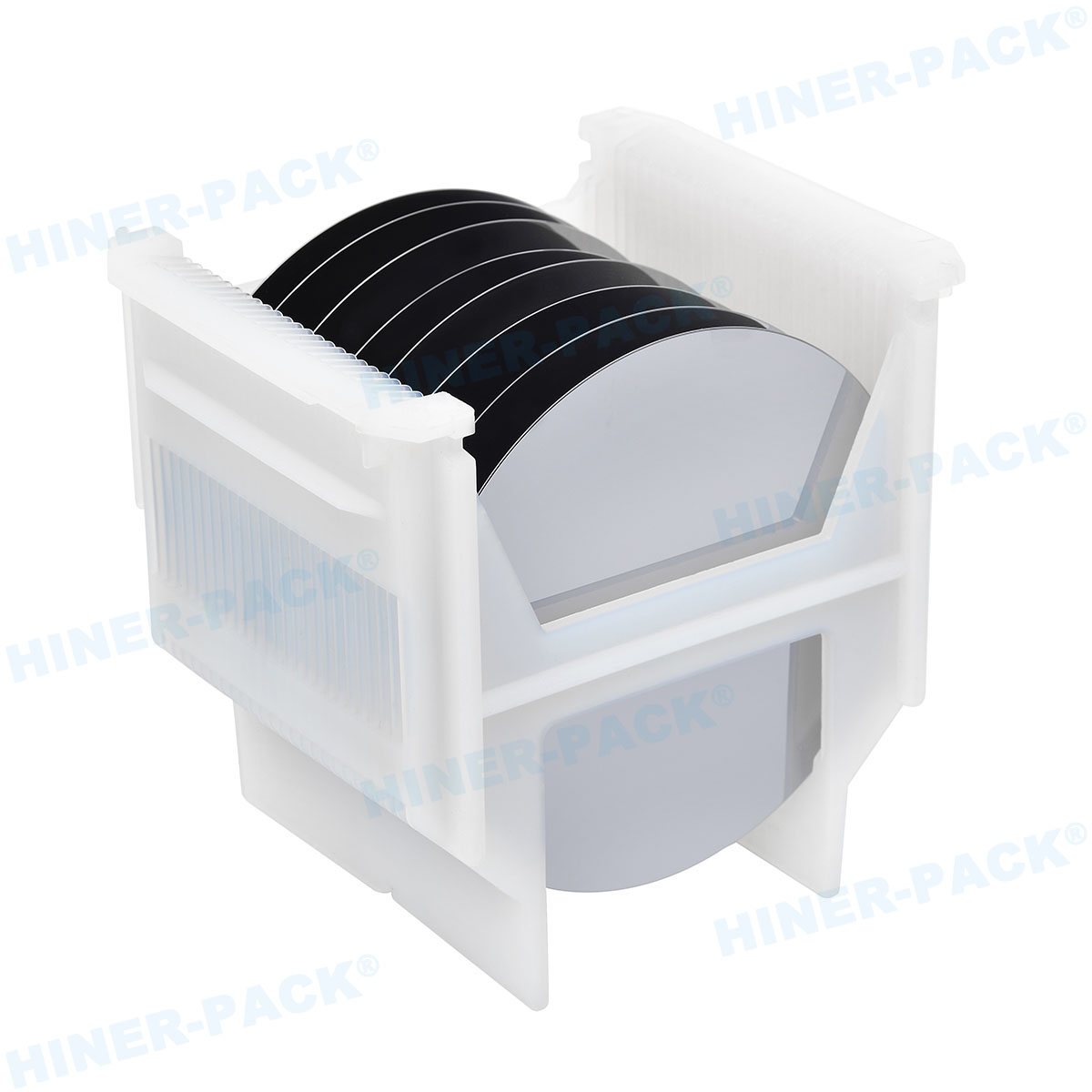
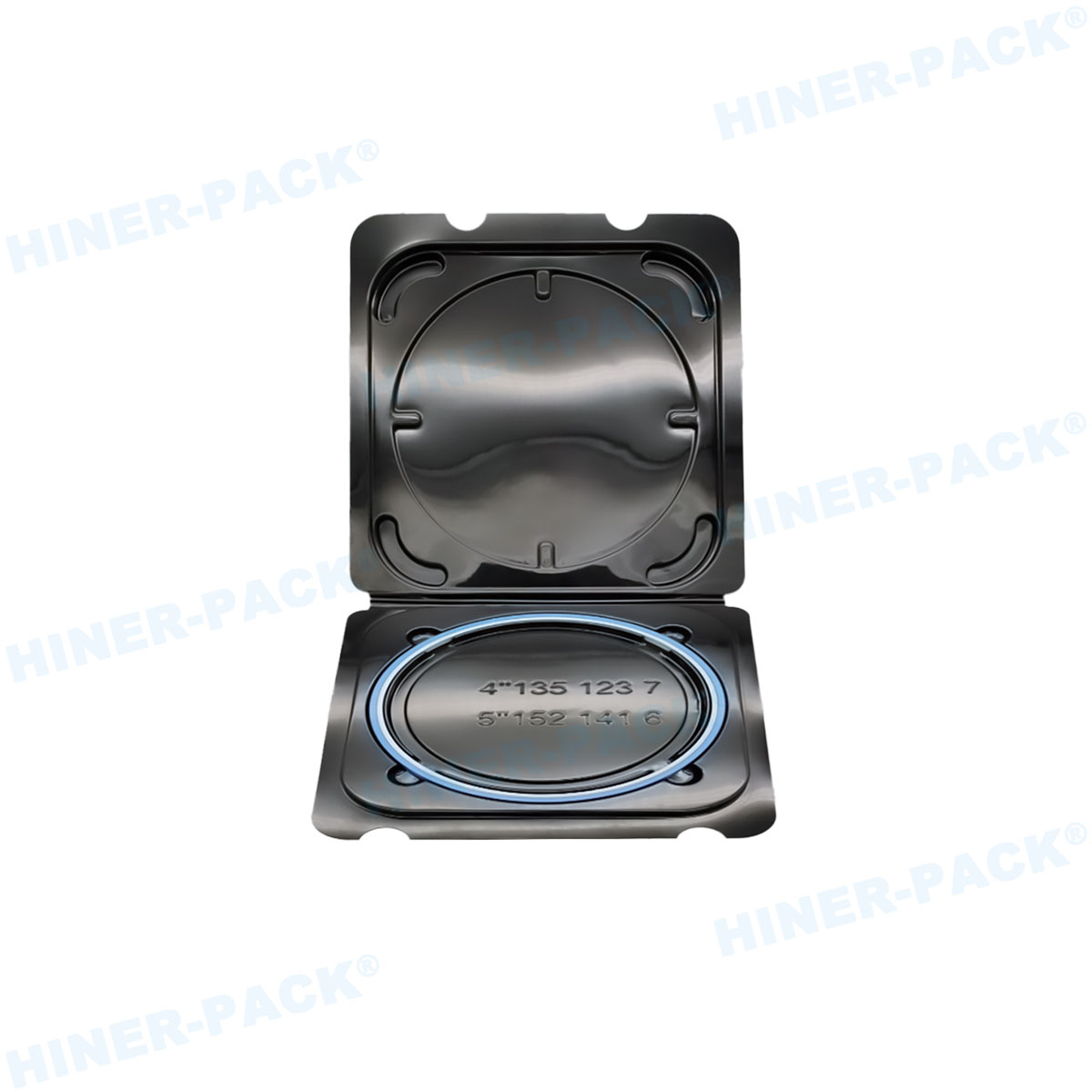
In the highly precise world of semiconductor manufacturing, the journey of a silicon wafer from fabrication to fabrication plant is fraught with potential peril. Microscopic contaminants, invisible to the naked eye, can spell disaster for yield rates and product reliability. This is where the humble yet critically important dust-free wafer shipper comes into play. Far more than a simple box, it is a high-tech safeguard, engineered to protect multi-million dollar wafer investments from the scourge of particulate contamination. But not all carriers are created equal. The true efficacy of a dust-free wafer shipper hinges on a trifecta of factors: the purity of its materials, the reliability of its latching mechanism, and the rigor of its particle certification. This article delves into the essential components, including the advanced PFA wafer shipper, robust latching mechanism wafer shipper designs, the critical importance of wafer shipper particle certification, and the definitive particle count test wafer shipper manufacturers employ to ensure integrity.

The Foundation of Cleanliness: Understanding the Dust-Free Wafer Shipper
A dust-free wafer shipper is a specialized container designed for the safe transportation and storage of silicon wafers, primarily between semiconductor manufacturing facilities. Its primary mission is to maintain the pristine cleanroom conditions the wafers were manufactured in, even in far less controlled environments like shipping docks and truck beds.
The concept of "dust-free" is relative and measured on a microscopic scale. In this context, "dust" refers to particles often smaller than a human hair (≤0.5 microns). These particles can originate from various sources: the environment, human handling, or, catastrophically, from the container itself through abrasion or outgassing. Therefore, a genuine dust-free wafer shipper is engineered to:
Minimize Particle Generation: Its materials must be non-shedding and resistant to abrasion.
Prevent Particle Ingress: Its design must create a secure, sealed barrier against the external environment.
Manage Electrostatic Discharge (ESD): It must be static-dissipative to avoid attracting airborne particles like a magnet.
Failure in any of these areas can lead to wafer contamination, resulting in defective chips, reduced yields, and significant financial losses.
PFA Wafer Shipper: The High-Purity Material Standard
When discussing high-performance carriers, the PFA wafer shipper represents a gold standard in material science. PFA (Perfluoroalkoxy alkane) is a specialized fluoropolymer that offers a unique set of properties ideal for protecting sensitive wafers.
Why is PFA the material of choice for ultra-clean applications?
Extremely Low Particle Generation: PFA is a remarkably inert and smooth polymer. Its non-stick surface and high resistance to abrasion mean it is very unlikely to shed particles through friction or wear-and-tear during repeated use and shipping.
Minimal Outgassing: PFA has exceptionally low levels of outgassing—the release of trapped gases or vapors from a material. This is critical because outgassed contaminants can condense on wafer surfaces, leading to hazing, crystal growth, or other defects during high-temperature processes.
Excellent Chemical Resistance: It is resistant to almost all industrial chemicals, ensuring the container itself won’t degrade when exposed to cleaning agents or accidental spills.
Inherent Static Dissipation: Many PFA-based shippers are formulated with carbon or other additives to provide permanent static-dissipative properties without the risk of shedding, unlike coated alternatives.
While other materials like polycarbonate or PP (polypropylene) are used, a PFA wafer shipper is often specified for the most critical processes, such as transporting advanced node wafers (e.g., 7nm, 5nm, and below) where even a single particle can ruin a die.
The Critical Role of a Reliable Latching Mechanism Wafer Shipper
The best materials are rendered useless if the container cannot seal properly. This is where the design of the latching mechanism wafer shipper becomes paramount. The latching mechanism is the gateway to the wafer-safe environment inside; if it fails, the seal is broken, and contamination is inevitable.
What defines an effective latching mechanism?
Consistent and Secure Seal: The mechanism must apply uniform pressure to the seal around the entire perimeter of the lid, ensuring no gaps for particles to enter. A robust latching mechanism wafer shipper will provide an audible or tactile "click" to confirm proper engagement.
Durability and Longevity: Latches must withstand thousands of cycles of opening and closing without wearing out, becoming loose, or—worst of all—generating particles themselves through metal-on-plastic friction.
Ease of Use: Operators wearing thick cleanroom gloves must be able to open and close the shipper easily and intuitively. A complicated mechanism increases the risk of improper sealing due to human error.
Material Compatibility: Metal springs or components must be carefully isolated to prevent them from contacting and scratching the carrier or, worse, the wafers inside. The best designs often use all-plastic, over-center latches that are cleanroom-friendly.
A failure in the latching mechanism is a common point of failure. A weak latch can pop open during transit, while an overly complex one can lead to operator error.
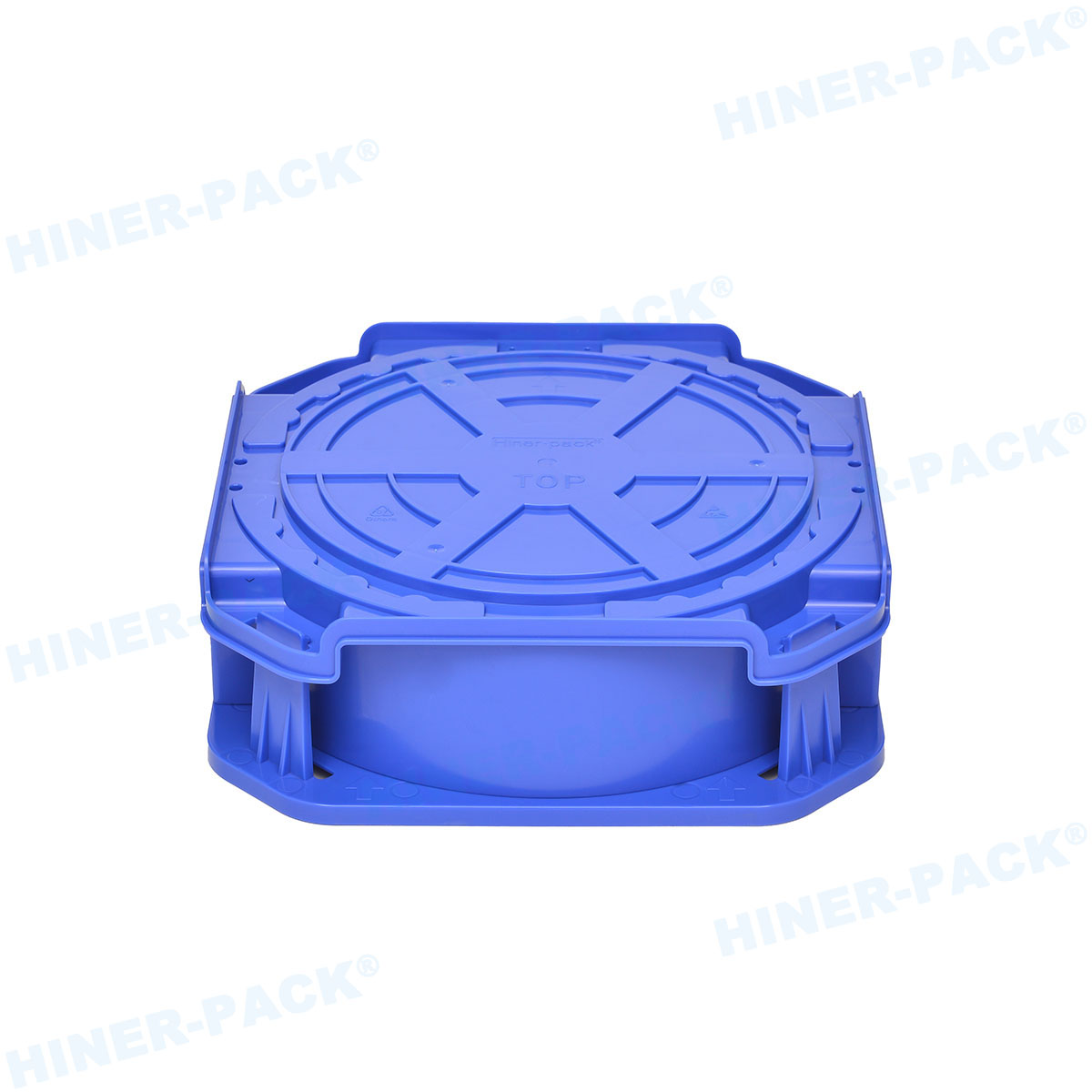

Proving Purity: The Importance of Wafer Shipper Particle Certification
How can a fab manager be sure that the shipper they are about to use is truly clean? They rely on data. Wafer shipper particle certification is the official documentation provided by the manufacturer that quantifies the container's cleanliness level.
This certification is the result of rigorous testing and provides essential data, including:
Particle Counts: The total number of particles added by the shipper at specific size thresholds (e.g., ≥0.3µm, ≥0.5µm).
Test Method: Reference to the exact industry standard used for testing (e.g., SEMI E1.5-0709).
Lot Traceability: The specific manufacturing lot the data corresponds to, ensuring consistency.
A proper wafer shipper particle certification is not a one-time generic spec sheet. Reputable manufacturers provide certificates of analysis (CoA) for specific production batches, giving users confidence in the consistency and quality of every unit they receive. Without this certification, you are essentially trusting a claim without evidence.
The Benchmark Test: How a Particle Count Test Wafer Shipper Works
The data on the certification sheet comes from one place: the particle count test wafer shipper. This is not a different product but refers to the standardized testing process that every reputable manufacturer performs.
The industry-standard methodology, often based on SEMI Standard E1.5-0709, involves a precise and repeatable procedure:
Preparation: The test shipper and a set of pristine monitor wafers are placed in a Class 1 or better cleanroom environment.
Initial Wafer Scan: The monitor wafers are meticulously scanned using a highly sensitive laser surface scanner to record a baseline particle count.
Loading and Simulation: The clean wafers are loaded into the dust-free wafer shipper. The closed shipper is then subjected to a simulated shipping environment. This typically involves agitating or vibrating the shipper in a controlled manner to simulate the stresses of transportation.
Final Wafer Scan: After the simulation, the wafers are carefully unloaded in the cleanroom and scanned again.
Analysis: The pre- and post-scan particle counts are compared. The difference, minus any environmental background contamination, is the particle adders attributable to the shipper itself.
A successful particle count test wafer shipper outcome shows very low, single-digit adders for particles at the specified sizes, proving the container's cleanliness.
Common Challenges and Problems with Wafer Shippers
Even with the best designs, issues can arise. Being aware of these common problems is key to prevention.
Latch Failure: As mentioned, this is a top concern. Latches can break, wear out, or simply not seal correctly over time. Solution: Implement regular inspection protocols and retire shippers with worn or damaged latches.
Material Degradation and Warping: Exposure to extreme temperatures (e.g., left in a hot truck) or harsh chemicals can cause plastic shippers to warp. A warped body can never form a proper seal, even with a good latch. Solution: Follow manufacturer guidelines for temperature limits and chemical compatibility.
Contamination from Improper Handling: The cleanest shipper in the world will become contaminated if handled incorrectly. Placing it on a dirty surface, opening it in a non-clean environment, or using non-cleanroom wipes for cleaning will introduce particles. Solution: Strict adherence to handling protocols and operator training.
Static Charge Buildup: A shipper with poor ESD protection can build up a charge, actively attracting airborne particles like a magnet. This negates the benefits of a physical seal. Solution: Ensure you are using shippers with permanent, static-dissipative properties.
False Confidence in "Clean" Packaging: Sometimes, the shipper is clean, but the plastic bags or foam used inside the shipping box are not. Particles from this packaging can migrate to the shipper's exterior and be introduced during opening. Solution: Only use packaging materials that meet the same cleanliness standards as the shipper.
Selecting the right container is not about choosing a single feature. It requires an integrated approach that considers all aspects of design and validation. A truly effective dust-free wafer shipper is the sum of its parts: the inherent purity of a PFA wafer shipper material, the unwavering security of a well-engineered latching mechanism wafer shipper, and the verifiable proof provided by a comprehensive wafer shipper particle certification based on a rigorous particle count test.
In the relentless pursuit of higher yields and smaller nodes, the margin for error evaporates. The choice of wafer packaging transitions from a simple logistical concern to a strategic decision directly impacting the bottom line. By understanding the technology, standards, and potential pitfalls, semiconductor manufacturers can make informed decisions to ensure their most valuable assets are protected every step of the way.