In the fast-paced world of semiconductor manufacturing, precision and efficiency are paramount. One often-overlooked component that plays a critical role in this industry is the 12 wafer cassette. This specialized container is designed to safely hold and transport 12 silicon wafers, which are the foundation of electronic devices like smartphones, computers, and automotive chips. As the demand for smaller, faster, and more powerful chips grows, understanding the 12 wafer cassette becomes essential for professionals in the field. This article delves into the key aspects of the 12 wafer cassette, highlighting its design, applications, and benefits in modern fabrication facilities. By exploring its multifaceted role, we can appreciate how this tool supports the seamless flow of wafer processing, minimizes contamination risks, and enhances overall productivity. Whether you're an engineer, a technician, or someone interested in semiconductor technology, this overview will provide valuable insights into why the 12 wafer cassette is a staple in cleanroom environments.

What is a 12 Wafer Cassette?
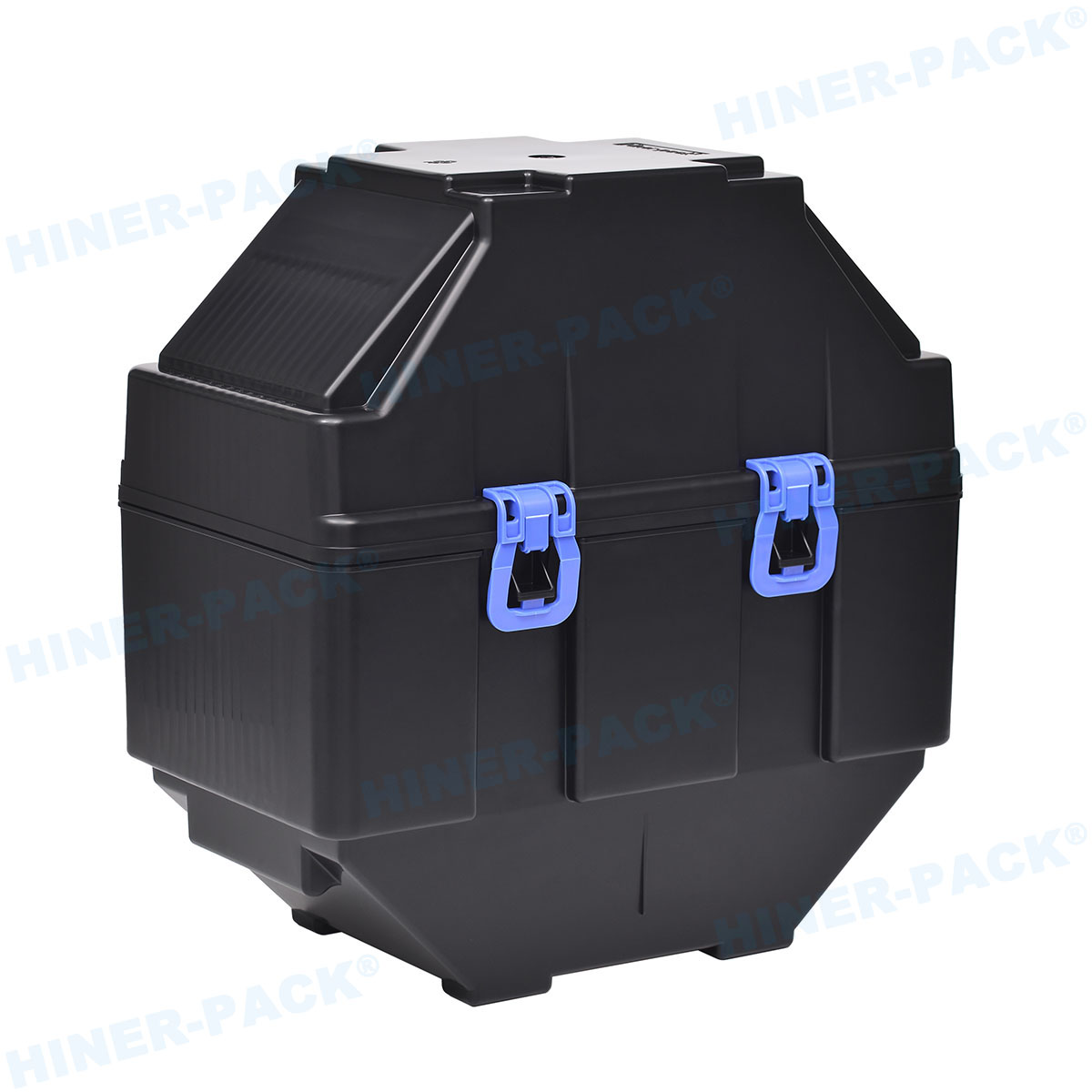
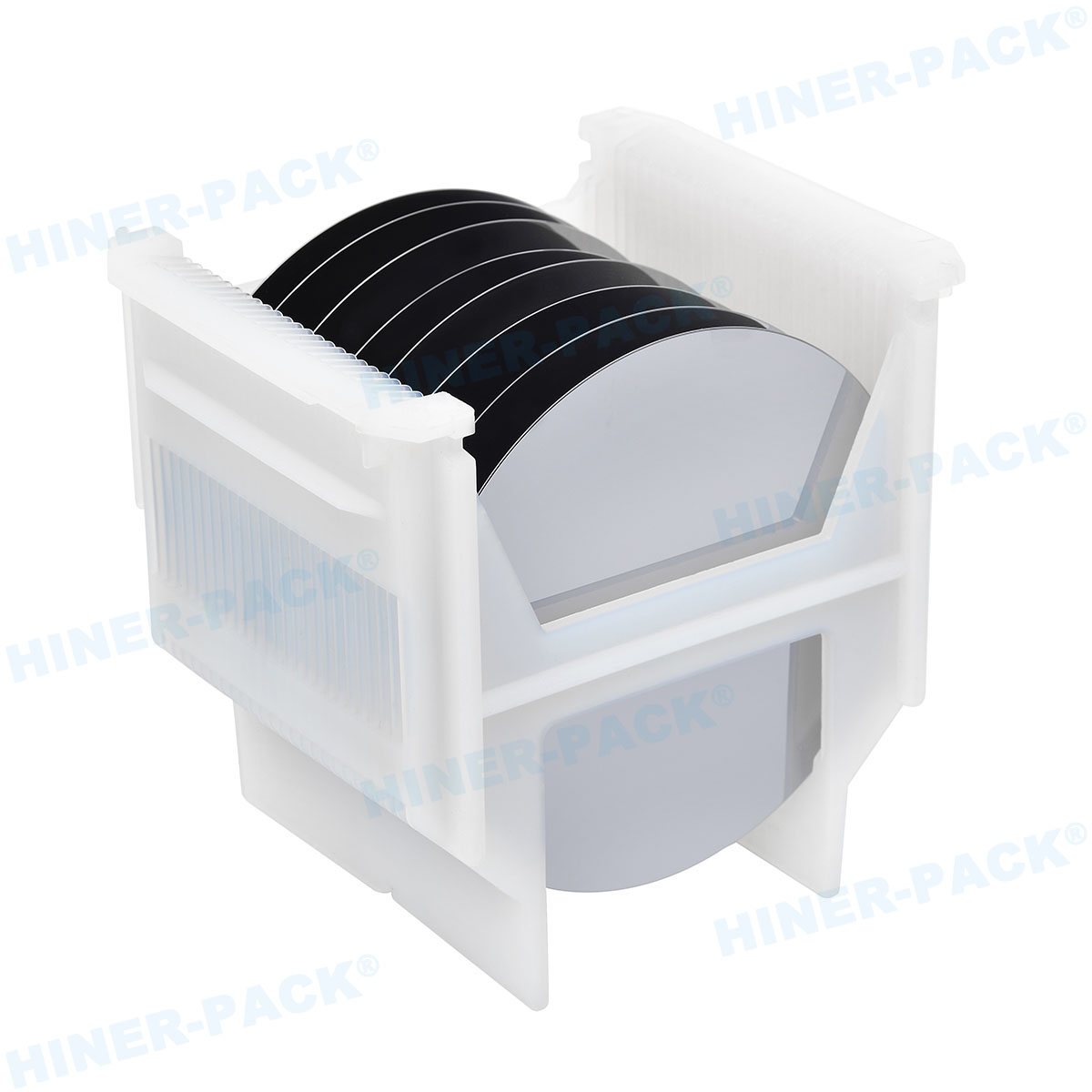
A 12 wafer cassette is a standardized container used in the semiconductor industry to store, transport, and handle up to 12 silicon wafers simultaneously. These wafers, typically made of silicon, are thin discs that serve as the substrate for integrated circuits. The cassette is engineered to protect the wafers from physical damage, contamination, and electrostatic discharge during various stages of manufacturing, such as lithography, etching, and doping. Made from high-purity materials like polycarbonate or other plastics that meet industry standards, the 12 wafer cassette features precisely spaced slots to hold each wafer securely without contact, preventing scratches or defects. Its compact size makes it ideal for automated handling systems, ensuring smooth integration into production lines. The term "12 wafer cassette" specifically refers to its capacity, which balances space efficiency with handling convenience, making it a popular choice for many fabrication plants. By using a 12 wafer cassette, manufacturers can maintain wafer integrity, reduce downtime, and streamline processes in high-volume environments. This tool is not just a container; it's a critical component that supports the entire chip-making ecosystem, from research labs to mass production facilities.
Design and Construction of the 12 Wafer Cassette
The design of a 12 wafer cassette is a marvel of engineering, focused on durability, cleanliness, and compatibility. Typically constructed from materials like polypropylene or PEEK (polyether ether ketone), these cassettes are resistant to chemicals, heat, and static buildup, which is crucial in sensitive cleanroom settings. Each cassette includes precisely molded slots that cradle the wafers—usually 200mm or 300mm in diameter—at uniform intervals, ensuring no physical contact between them. This minimizes the risk of particulate contamination, a major concern in semiconductor fabrication. The cassette often features a front-opening mechanism for easy access, along with handles or robotic interface points for automated retrieval and placement. Ventilation holes may be incorporated to allow for proper airflow during cleaning processes, such as purging with inert gases. Additionally, the 12 wafer cassette is designed to stack neatly with other cassettes, optimizing storage space in wafer carriers or stockers. Color coding and labeling options help in identifying wafer types or process stages, enhancing traceability. Overall, the robust construction of the 12 wafer cassette ensures it can withstand repeated use in harsh environments, while its ergonomic design supports both manual and robotic handling, contributing to a more efficient and error-free manufacturing workflow.
Applications in Semiconductor Manufacturing
In semiconductor manufacturing, the 12 wafer cassette serves as a backbone for wafer logistics across multiple processes. From the initial wafer preparation to final inspection, this cassette facilitates the movement of wafers through steps like chemical mechanical planarization (CMP), deposition, and metrology. For instance, in a typical fab line, wafers are loaded into a 12 wafer cassette after being sliced from a silicon ingot, then transported to cleaning stations where contaminants are removed. During photolithography, the cassette ensures wafers are delivered to exposure tools without misalignment. Its compatibility with automated material handling systems (AMHS) allows for seamless integration, reducing human intervention and the associated contamination risks. The 12 wafer cassette is also pivotal in batch processing, where multiple wafers undergo simultaneous treatments, such as in diffusion furnaces. This not only speeds up production but also maintains consistency in chip quality. Moreover, in testing and packaging phases, the cassette helps organize wafers for electrical testing and dicing. By enabling a controlled flow, the 12 wafer cassette minimizes bottlenecks and enhances yield rates, making it indispensable for high-throughput facilities aiming to meet tight deadlines and quality standards.
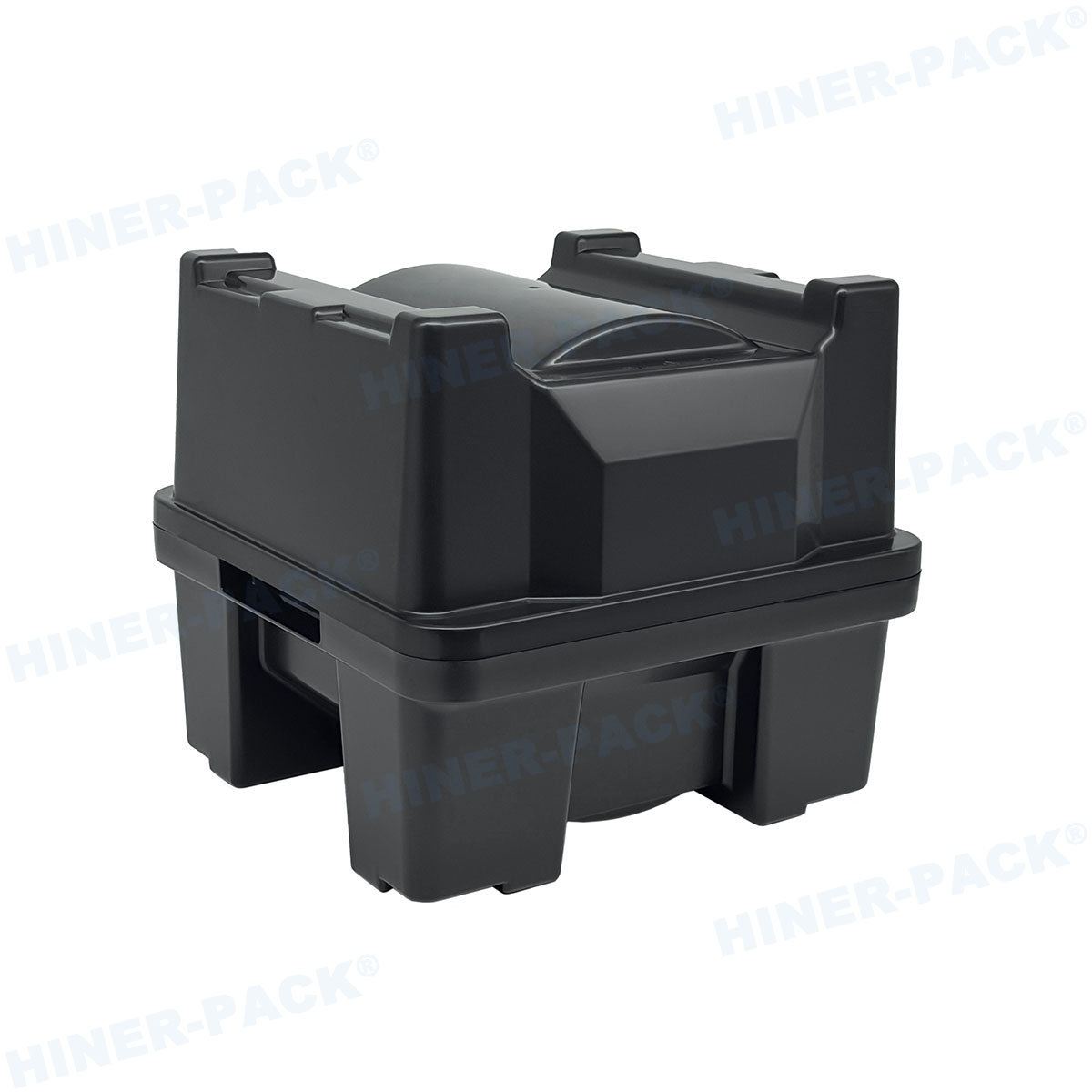

Advantages of Using a 12 Wafer Cassette
The adoption of a 12 wafer cassette brings numerous advantages to semiconductor operations. Firstly, its capacity strikes a balance between handling efficiency and space utilization; unlike larger cassettes that might be cumbersome, the 12 wafer cassette allows for manageable loads that reduce the risk of damage during transport. This leads to higher wafer yields and lower rejection rates. Secondly, the cassette's design promotes contamination control—by keeping wafers isolated in individual slots, it prevents cross-contamination and particulate accumulation, which is critical for achieving nanoscale precision in chip features. Thirdly, the 12 wafer cassette enhances automation compatibility, enabling faster cycle times and reduced labor costs. In terms of cost-effectiveness, its standardized size means it can be used across various equipment brands, minimizing the need for custom solutions. Additionally, the cassette supports better inventory management, as it allows for easy tracking of wafer lots through barcodes or RFID tags. From a safety perspective, the 12 wafer cassette reduces manual handling errors, protecting both the wafers and operators. Overall, these benefits contribute to a more resilient and scalable manufacturing process, helping companies stay competitive in the dynamic semiconductor market.
Standards and Compliance for 12 Wafer Cassettes
To ensure interoperability and quality, 12 wafer cassettes must adhere to strict industry standards, primarily set by organizations like SEMI (Semiconductor Equipment and Materials International). SEMI standards, such as SEMI E1.9 for cassette dimensions and SEMI E105 for material purity, define the specifications for a 12 wafer cassette, including slot pitch, overall dimensions, and material properties. Compliance with these standards guarantees that the cassette fits seamlessly into equipment from different manufacturers, such as wafer steppers or etchers. Moreover, regulations concerning electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection and chemical resistance are enforced to prevent wafer damage in sensitive environments. For instance, a 12 wafer cassette may need to meet SEMI E129 guidelines for handling in high-temperature processes. Certification processes often involve testing for particulate generation, mechanical strength, and cleanliness levels. By following these standards, manufacturers of 12 wafer cassettes ensure reliability and safety, which in turn supports global supply chain consistency. This adherence not only fosters innovation but also helps facilities pass audits and maintain certifications like ISO 9001, reinforcing trust in the semiconductor ecosystem.
Maintenance and Cleaning Best Practices
Proper maintenance of a 12 wafer cassette is vital for prolonging its lifespan and ensuring wafer integrity. Regular cleaning procedures involve using ultra-pure water, isopropyl alcohol, or specialized solvents to remove residues and particles. Automated cleaning systems, such as wet benches or spray units, are commonly employed to handle a 12 wafer cassette without introducing contaminants. It's recommended to clean the cassette after each use or based on a scheduled maintenance plan, depending on the process environment. Inspection for cracks, warping, or slot damage should be performed routinely, as any defect can compromise wafer safety. Storage in controlled environments, away from dust and humidity, helps maintain the cassette's condition. Additionally, handling a 12 wafer cassette with cleanroom-compatible gloves and tools minimizes human-induced contamination. For electrostatic sensitive applications, using antistatic bags or ionizers during storage is advisable. By implementing these best practices, companies can reduce downtime, avoid costly wafer losses, and uphold the high standards required in semiconductor fabrication. A well-maintained 12 wafer cassette not only supports efficient production but also contributes to sustainable operations by reducing waste.
Future Trends and Innovations
The evolution of the 12 wafer cassette is closely tied to advancements in semiconductor technology. As chips shrink to 5nm and below, cassettes are being redesigned to handle thinner wafers and new materials, such as gallium nitride or silicon carbide. Innovations include smart 12 wafer cassettes embedded with sensors for real-time monitoring of temperature, humidity, and vibration during transport. This data can be integrated with IoT platforms to predictive maintenance and optimize logistics. Another trend is the development of lightweight, recyclable materials to enhance sustainability without compromising performance. Additionally, with the rise of 3D chip stacking, the 12 wafer cassette may see modifications to accommodate multi-layer wafers. Collaboration between cassette manufacturers and equipment vendors is driving standardization for next-generation fabs, ensuring that the 12 wafer cassette remains a key enabler of efficiency. As the industry moves toward more automated and flexible manufacturing, the humble 12 wafer cassette will continue to adapt, playing a crucial role in the future of electronics.
In summary, the 12 wafer cassette is an indispensable tool in semiconductor manufacturing, offering a blend of precision, durability, and efficiency. From its thoughtful design to its adherence to global standards, this cassette supports the entire wafer journey, ensuring that the chips powering our world are produced with the highest quality. By embracing best practices and staying abreast of innovations, industry professionals can leverage the 12 wafer cassette to drive progress and meet the ever-growing demands of technology.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What is the primary purpose of a 12 wafer cassette?
A1: The primary purpose of a 12 wafer cassette is to safely store, transport, and handle up to 12 silicon wafers in semiconductor manufacturing processes. It protects wafers from contamination, physical damage, and electrostatic discharge, ensuring they remain intact and clean during various fabrication stages like etching, deposition, and inspection.
Q2: How does a 12 wafer cassette differ from other cassette sizes?
A2: A 12 wafer cassette differs from other sizes, such as 25-wafer cassettes, primarily in its capacity and handling efficiency. The 12 wafer cassette is often preferred for its balance between load size and ease of use, making it ideal for processes requiring moderate batch sizes and reduced risk of mishandling. It also tends to be more compact, fitting well in automated systems without overwhelming space constraints.
Q3: What materials are commonly used in manufacturing a 12 wafer cassette?
A3: Common materials for a 12 wafer cassette include high-purity plastics like polycarbonate, polypropylene, or PEEK (polyether ether ketone). These materials are chosen for their chemical resistance, low particulate generation, and ability to withstand high temperatures and static charges, meeting industry standards for cleanroom compatibility and durability.
Q4: How often should a 12 wafer cassette be cleaned and maintained?
A4: A 12 wafer cassette should be cleaned after each use or according to a regular maintenance schedule, typically based on the contamination level of the operating environment. Daily or weekly inspections for damage and cleaning with ultra-pure water or solvents are recommended to prevent residue buildup and ensure optimal performance in semiconductor fabrication.
Q5: Can a 12 wafer cassette be used with automated handling systems?
A5: Yes, a 12 wafer cassette is designed to be compatible with automated material handling systems (AMHS) in semiconductor fabs. It features standardized dimensions and interface points that allow robots to efficiently load, unload, and transport the cassette, reducing manual labor and enhancing production speed and accuracy.