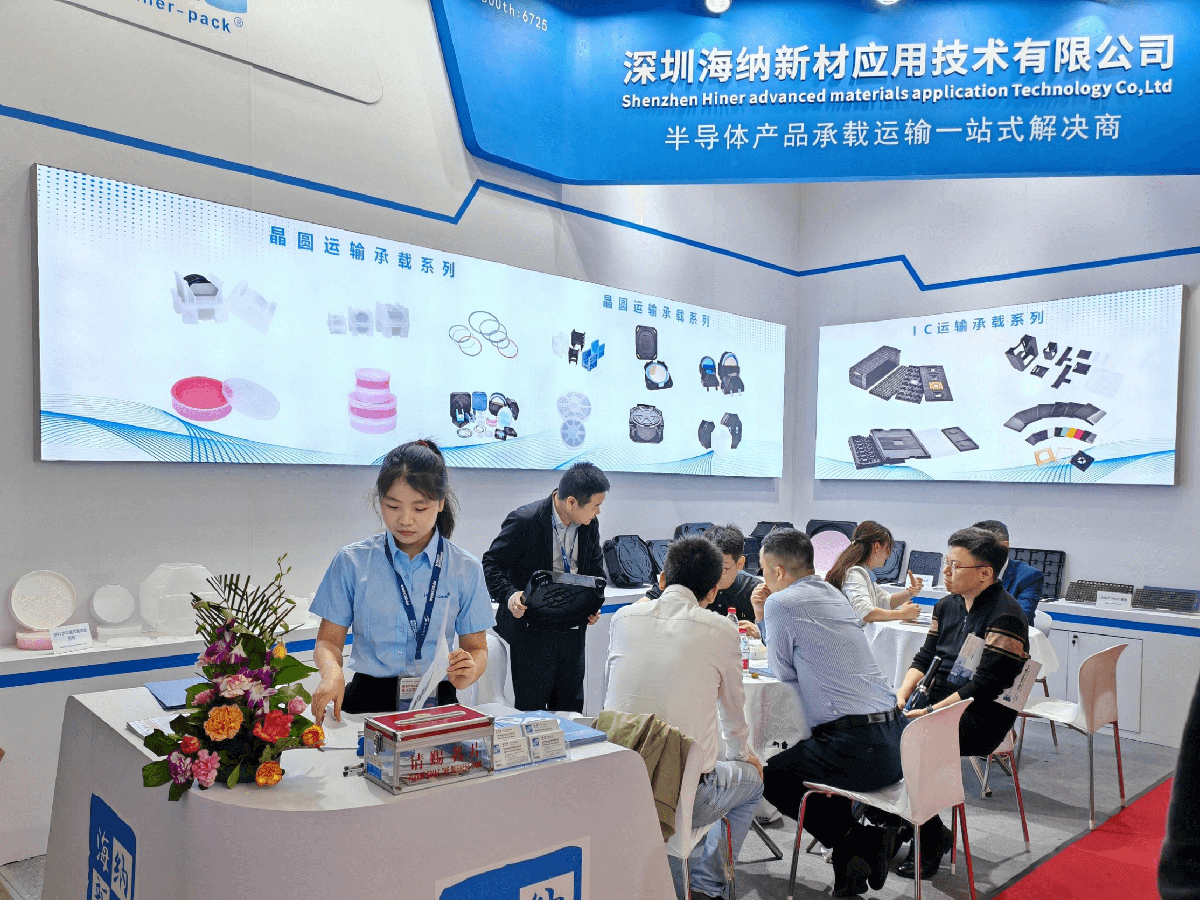
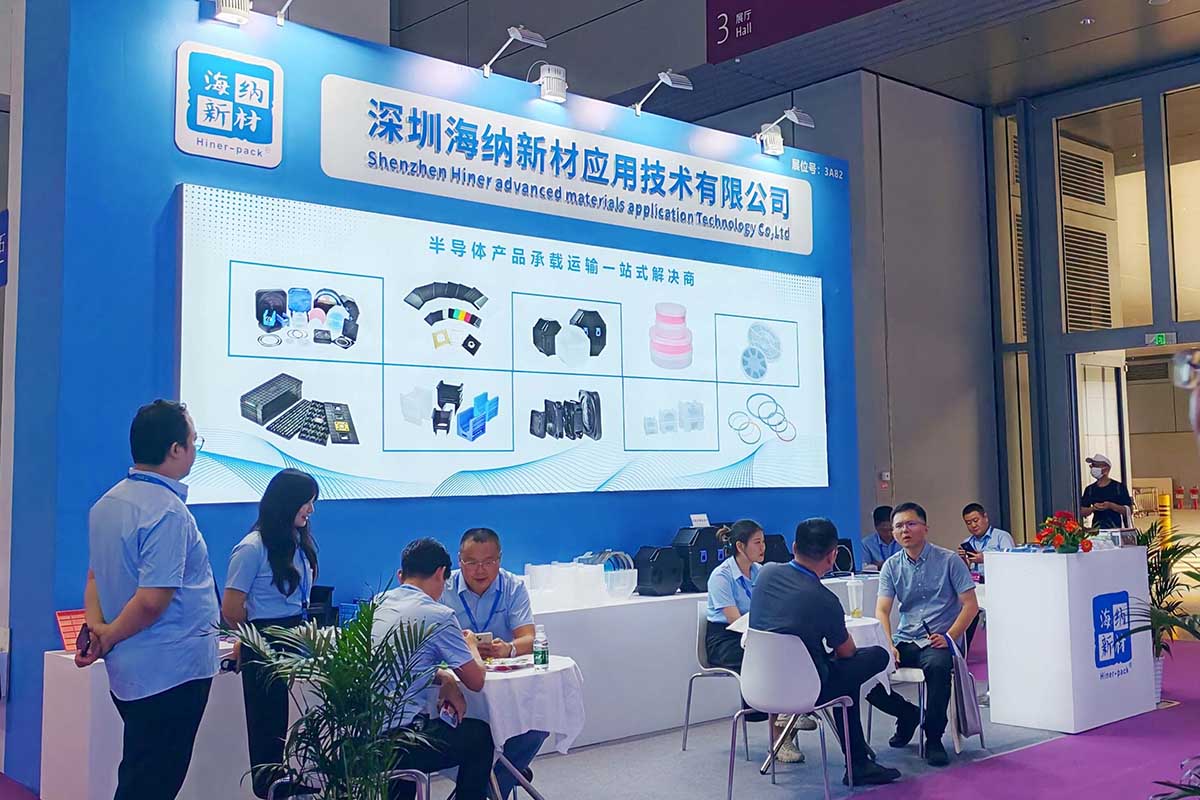
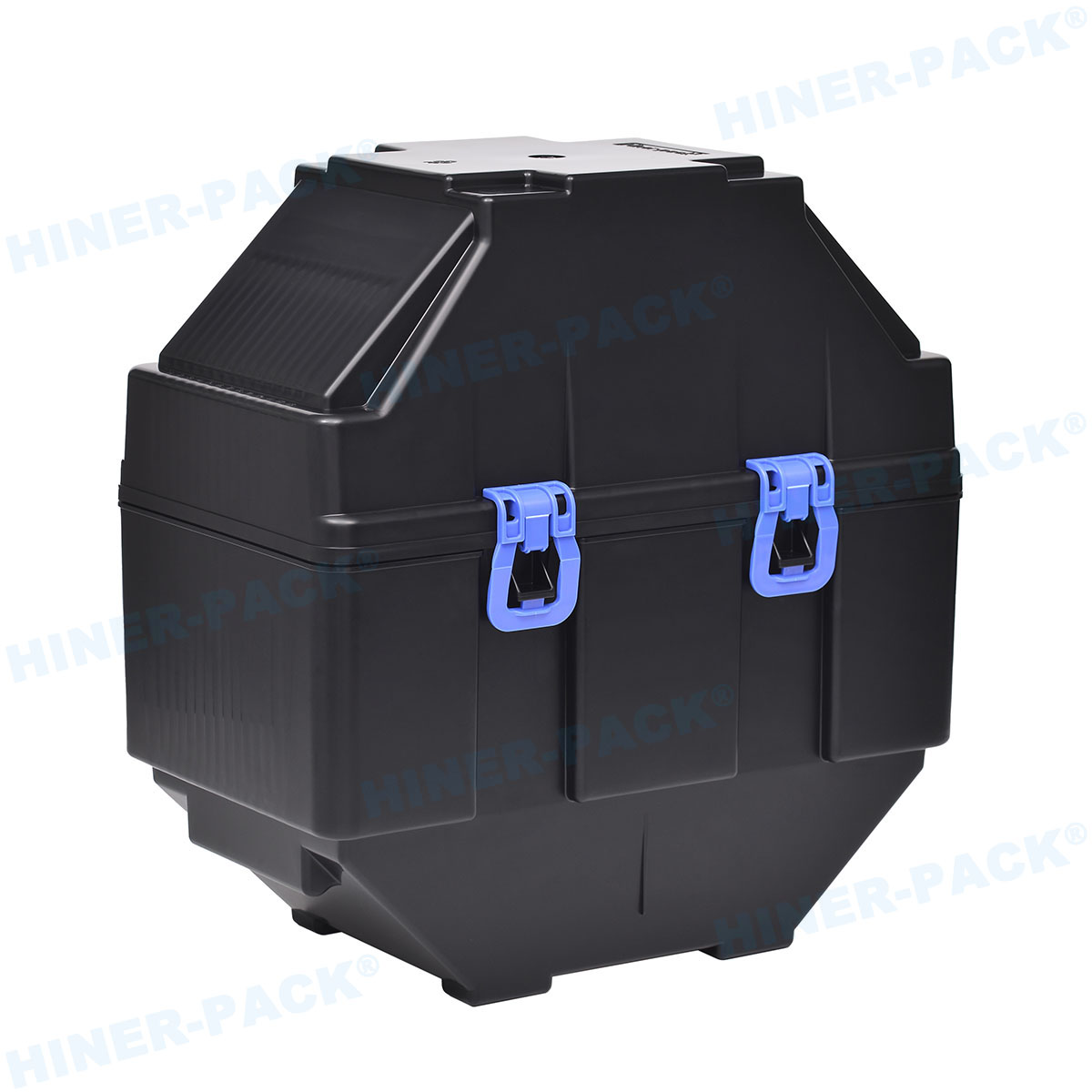
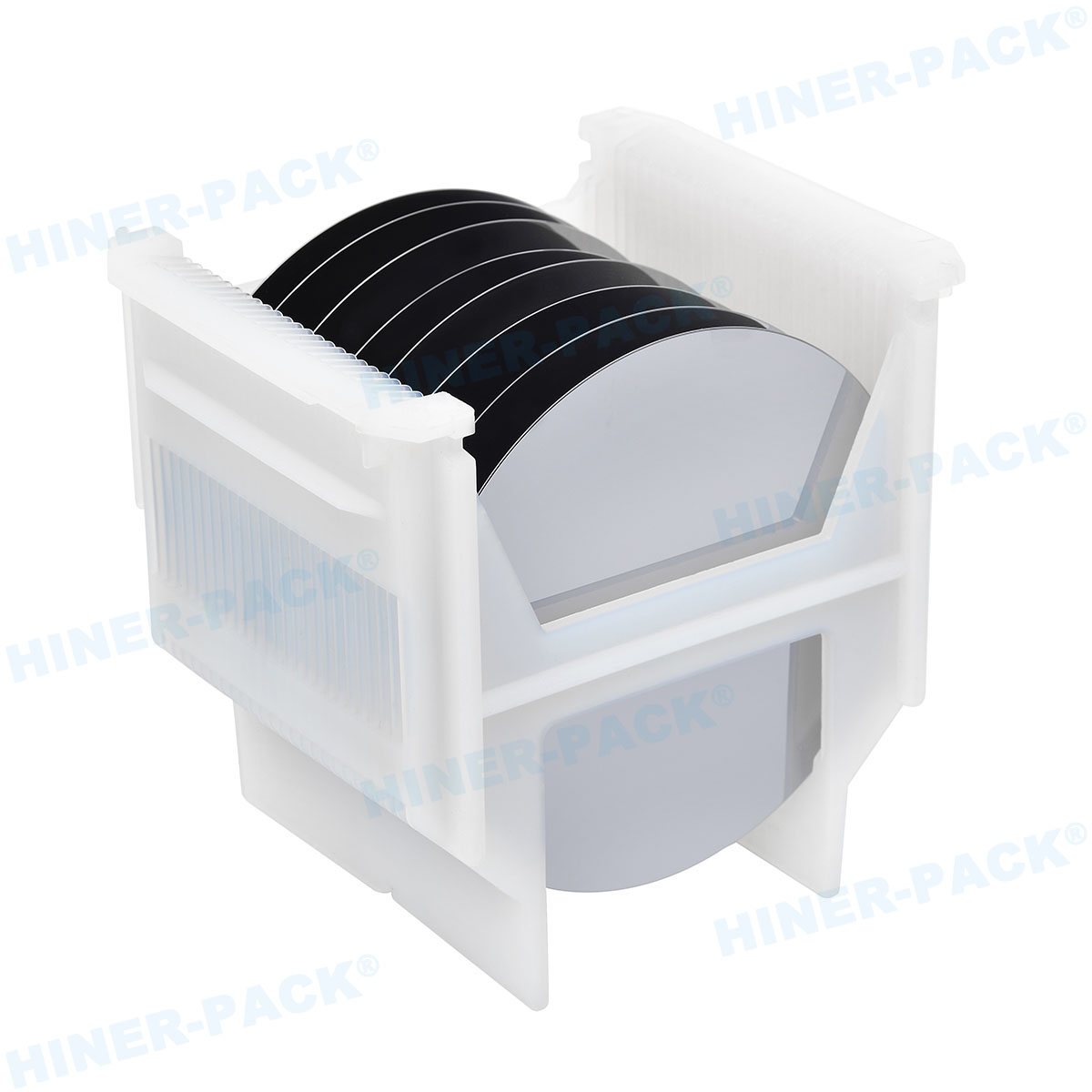
The safe transport of silicon wafers is not an afterthought in the semiconductor industry; it’s a critical step in the supply chain. A single scratch, particle contamination, or electrostatic discharge during shipping can ruin millions of dollars worth of product.
This makes the choice of your wafer shipper supplier one of the most important decisions for protecting yield and profit. The right partner provides more than just a box; they deliver security, reliability, and peace of mind.
Companies like Hiner-pack have built their reputation on understanding these high-stakes requirements, engineering solutions that meet the rigorous demands of global fabs and OSATs. Let’s break down the five essential factors you must evaluate when selecting a wafer shipper supplier.
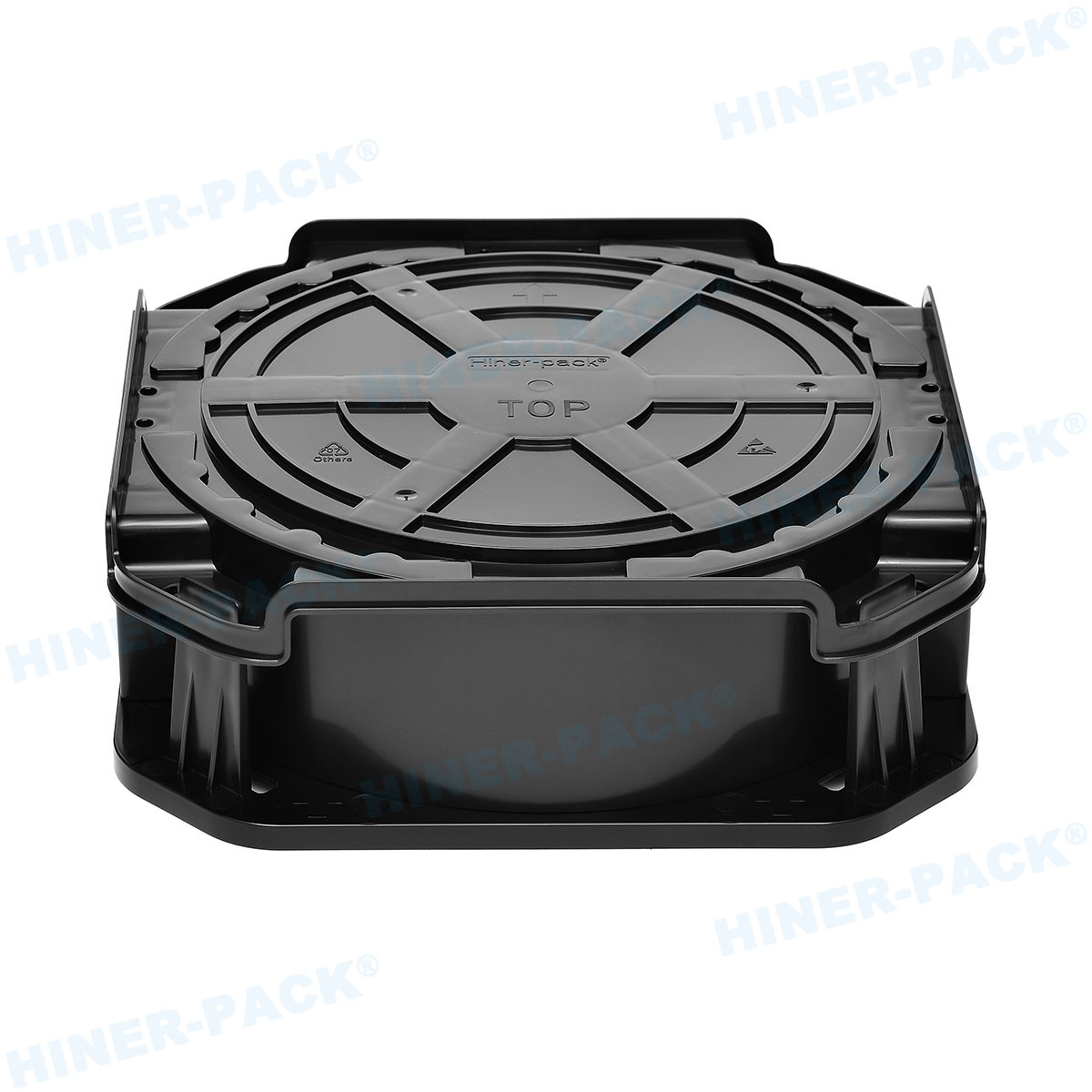

What Exactly is a Wafer Shipper?
Before diving into selection criteria, let's define the product. A wafer shipper is a specialized, high-precision container designed to protect wafers during inter-facility transport, international shipping, or long-term storage.
Unlike in-fab cassettes, these are ruggedized, sealed units that shield wafers from physical shock, vibration, moisture, and airborne contaminants. They are the first and last line of defense for your delicate substrates outside the cleanroom.
Your wafer shipper supplier must master the design, materials, and manufacturing of these vital carriers. The goal is zero added defects from point A to point B.
Factor 1: Material Purity and Contamination Control
The materials in direct contact with wafers are paramount. A top-tier wafer shipper supplier uses only certified, low-outgassing polymers and composites.
Key considerations include:
Particle Generation: Surfaces must be smooth and resistant to abrasion. Any shedding during transit or handling is unacceptable.
Chemical Stability: Materials must not off-gas volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that could deposit on wafer surfaces, affecting subsequent processes.
Static Control: Inherently static-dissipative or conductive materials are crucial to prevent Electrostatic Discharge (ESD), which can damage integrated circuits.
Suppliers should provide material certification data sheets to back up their claims.
Factor 2: Mechanical Protection and Design Integrity
A shipper must survive the rigors of global logistics. It’s not just about a sturdy outer shell.
Cushioning System: The internal mechanism that cradles the wafer cassette is critical. It must securely grip the cassette while absorbing vibrations and shock loads from handling. Look for designs with proven performance in standardized ISTA (International Safe Transit Association) tests.
Seal Reliability: The environmental seal is what keeps moisture and particles out. A consistent, reliable gasket or sealing mechanism is non-negotiable. The closure should be secure yet user-friendly for operators.
Stackability and Handling: In warehouses and during transport, shippers are stacked. The design must ensure stability and prevent crushing. Ergonomic features for safe manual handling are also a plus.
Factor 3: Cleanroom Compatibility and Process Integration
The best shipper is one that integrates smoothly into your existing workflow. Your chosen wafer shipper supplier should understand fab protocols.
Cleanroom Assembly: High-quality suppliers assemble their shippers in controlled environments (often Class 100 or better) to ensure they ship to you in a ready-to-use, particle-free state.
Cassette Compatibility: The shipper must be designed to perfectly interface with standard SEMI (Semiconductor Equipment and Materials International) cassettes (FOUPs, FOSBs, etc.) without forcing or misalignment.
Ease of Decontamination: Can the shipper be easily cleaned or baked out for re-use? A design that facilitates decontamination extends product life and reduces total cost of ownership.
Hiner-pack, for instance, focuses on this seamless integration, ensuring their shippers are not just protective vessels but efficient components within the larger manufacturing flow.
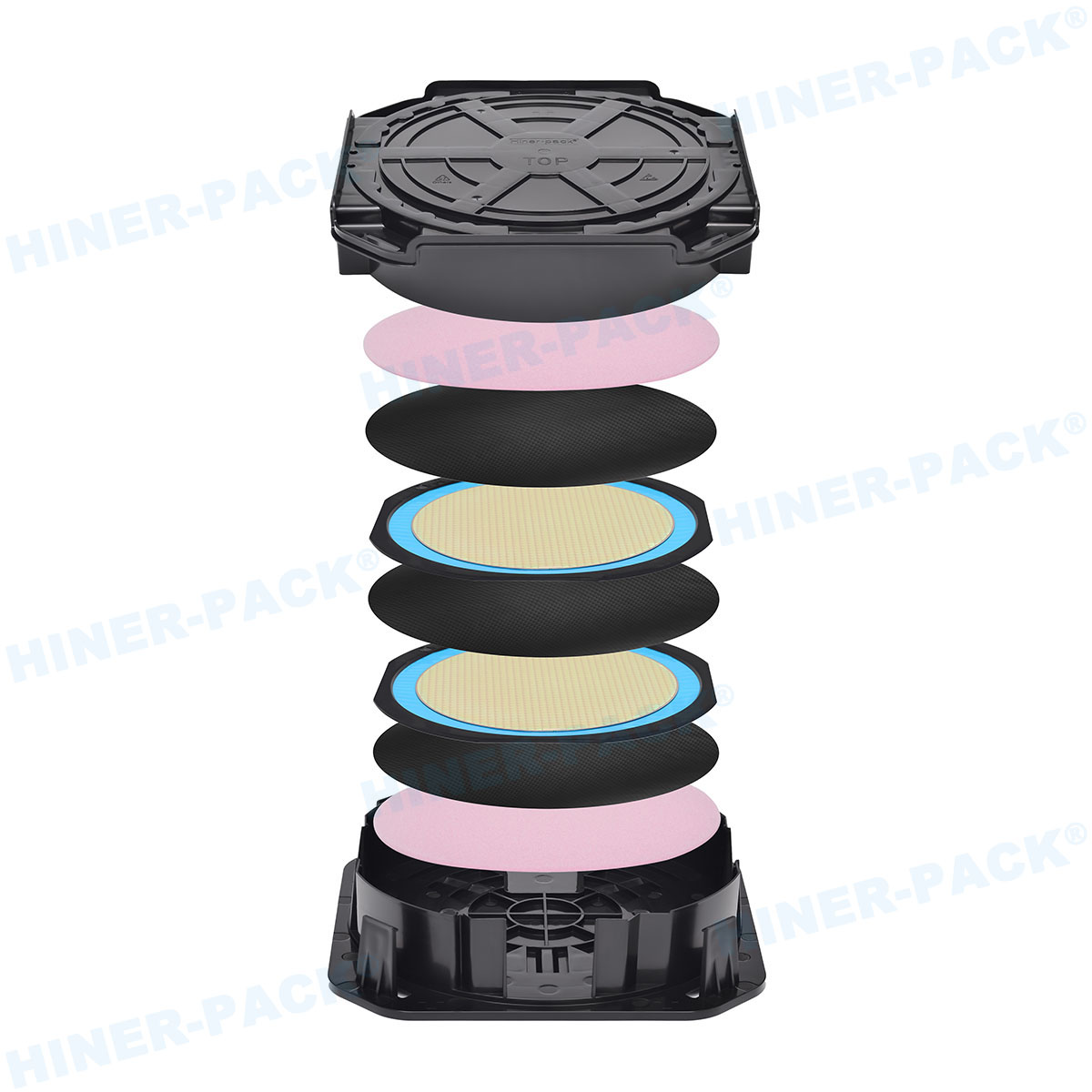

Factor 4: Certifications and Quality Management Systems
In an industry governed by standards, paperwork matters. A reputable supplier’s commitments are validated by their certifications.
Insist on suppliers with:
ISO 9001: The baseline for quality management systems.
ISO 14001: Demonstrates environmental management responsibility.
SEMI Standards Compliance: Adherence to relevant SEMI standards (e.g., for materials, dimensions, and safety) is a clear indicator of industry-specific expertise.
Documentation Traceability: They should provide full traceability for materials and manufacturing lots.
This formalized approach to quality is your best guarantee of consistent, reliable product performance batch after batch.
Factor 5: Global Support and Customization Capability
Your needs may be unique. A supplier’s ability to support you locally and adapt to your requirements is a major differentiator.
Customization: Can they modify shipper dimensions for non-standard wafer sizes or custom cassettes? Can they add RFID tagging, specific branding, or unique sealing mechanisms?
Global Logistics: Do they have manufacturing or distribution hubs in key semiconductor regions (Asia, North America, Europe) to ensure timely supply and reduce shipping costs and lead times?
Technical Support: Do they offer engineering support to solve specific packaging or handling challenges? A collaborative supplier acts as a partner, not just a vendor.
The Long-Term Value of the Right Partnership
Choosing a wafer shipper supplier is not a simple procurement task. It’s a strategic partnership. The lowest-cost option often carries hidden expenses: yield loss, containment actions, and supply chain delays.
Investing in a supplier that excels in material science, robust design, quality systems, and support pays dividends in protected yields, operational efficiency, and reduced risk. It’s an investment in safeguarding your most valuable assets.
As you evaluate potential partners, consider how their philosophy aligns with your need for absolute precision and reliability. Industry leaders like Hiner-pack have demonstrated that a deep focus on these five factors forms the foundation of a trusted supplier relationship, ensuring that your wafers are secure at every stage of their journey.
FAQ: Wafer Shipper Supplier Selection
Q1: What is the biggest risk of choosing a low-cost wafer shipper supplier?
A1: The biggest risk is latent yield loss due to contamination (particles, outgassing) or physical damage that isn't discovered until later processing stages. This can lead to costly scrapping of partially finished wafers, far outweighing any initial savings on the shipper itself.
Q2: Are all wafer shippers compatible with automated material handling systems (AMHS)?
A2: No, compatibility varies. While many are designed for manual handling, specific models are built to interface with AMHS. You must clearly communicate this requirement to your wafer shipper supplier to ensure the design includes the correct dimensions, gripping features, and identification markers (like barcodes) for your system.
Q3: How many times can a wafer shipper typically be reused?
A3: Reuse cycles depend heavily on the shipper's build quality, the rigor of the transport environment, and the facility's decontamination procedures. High-quality shippers from reputable suppliers can often withstand dozens of cycles if properly inspected, cleaned, and maintained. Your supplier should provide guidelines for inspection and end-of-life criteria.
Q4: What certifications should I prioritize when auditing a potential wafer shipper supplier?
A4: Prioritize ISO 9001 for quality management and evidence of compliance with relevant SEMI standards (e.g., SEMI E1.9 for mechanical specifications). ISO 14001 is also valuable for environmental stewardship. Material-specific certifications like USP Class VI or low-outgassing data reports are critical for contamination control.
Q5: Can a supplier help with validating a new wafer shipper for our specific process?
A5: A capable and collaborative wafer shipper supplier should offer support in the validation process. This can include providing detailed material data, supporting Design of Experiments (DOE), or offering trial units for your internal testing under real-world shipping and handling conditions.