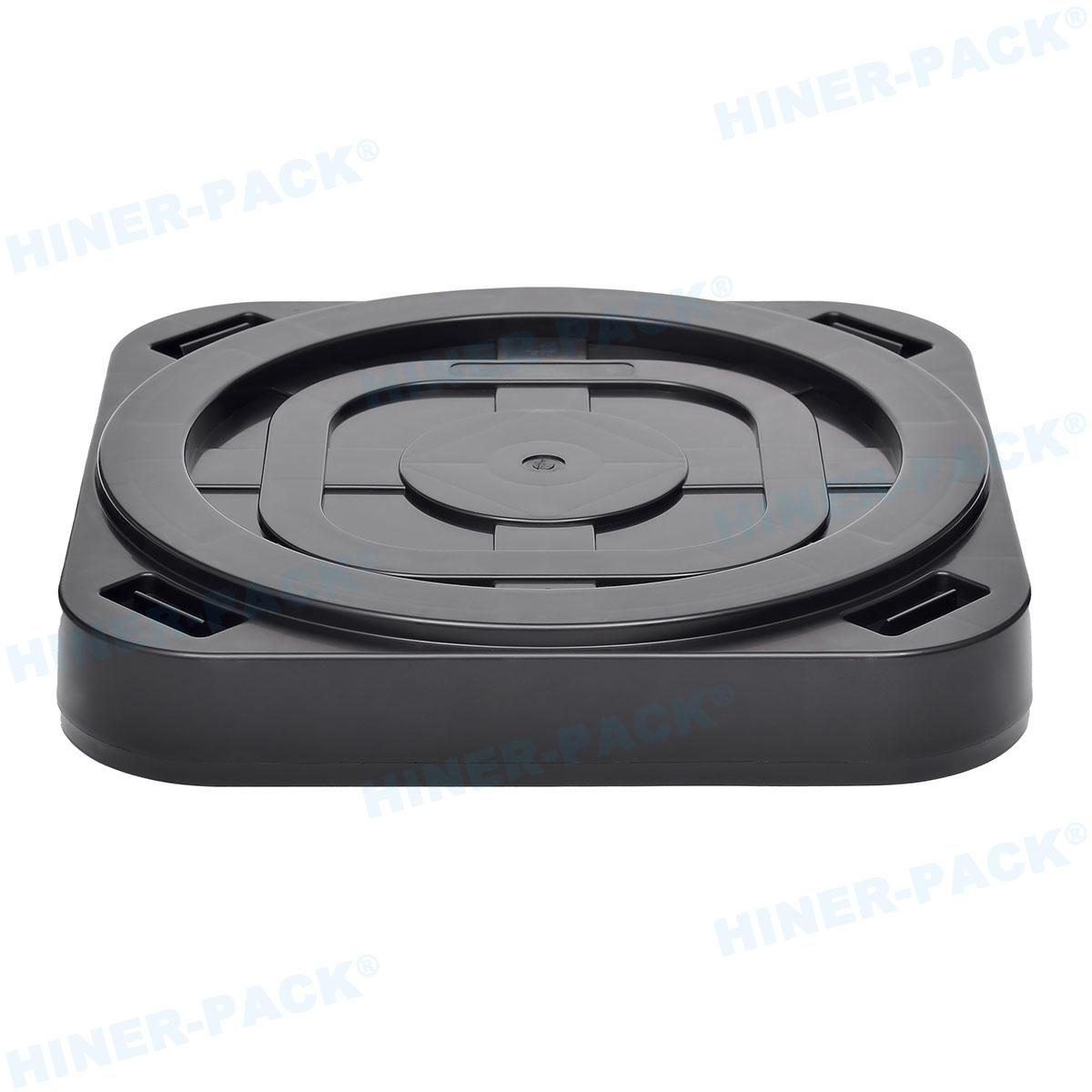
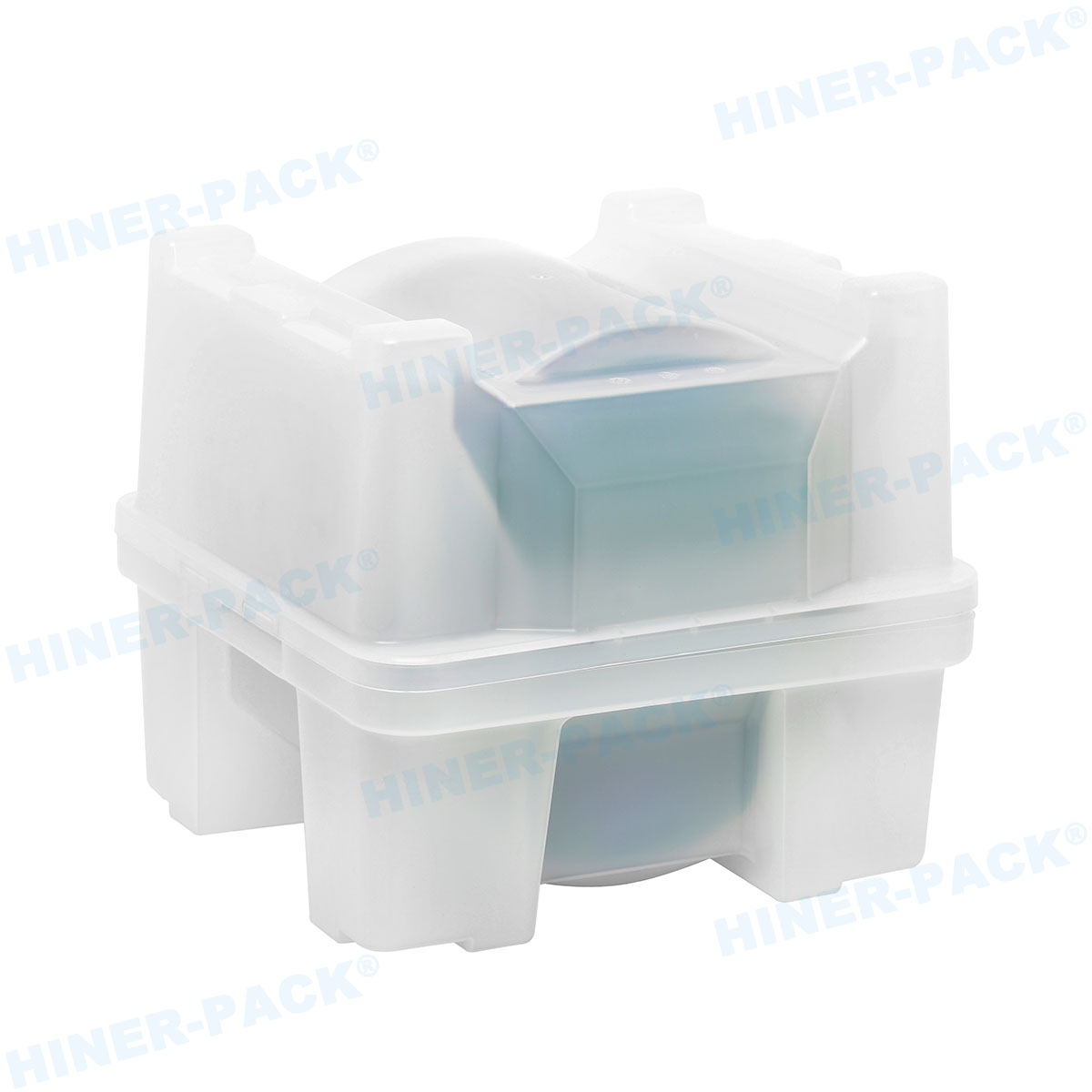
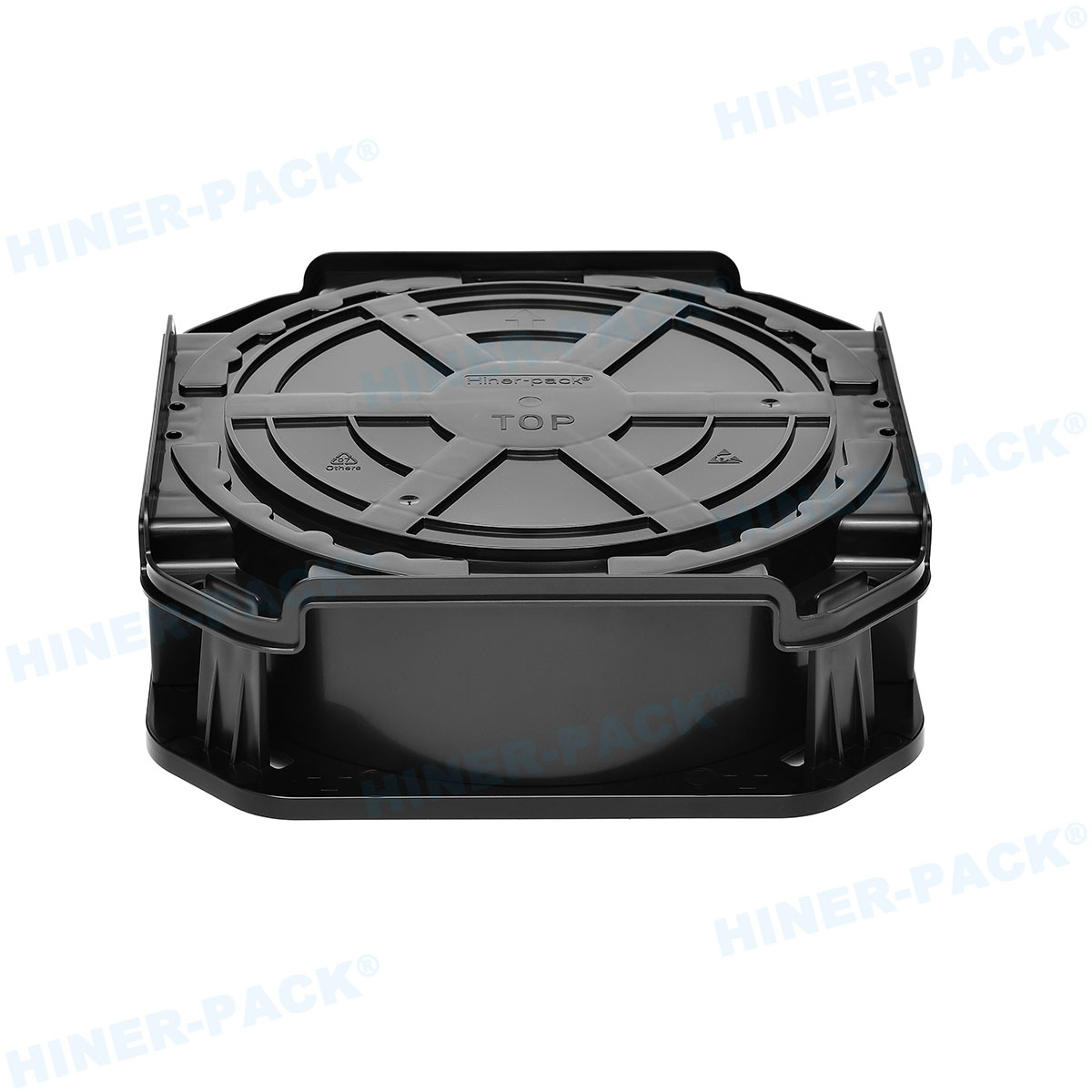
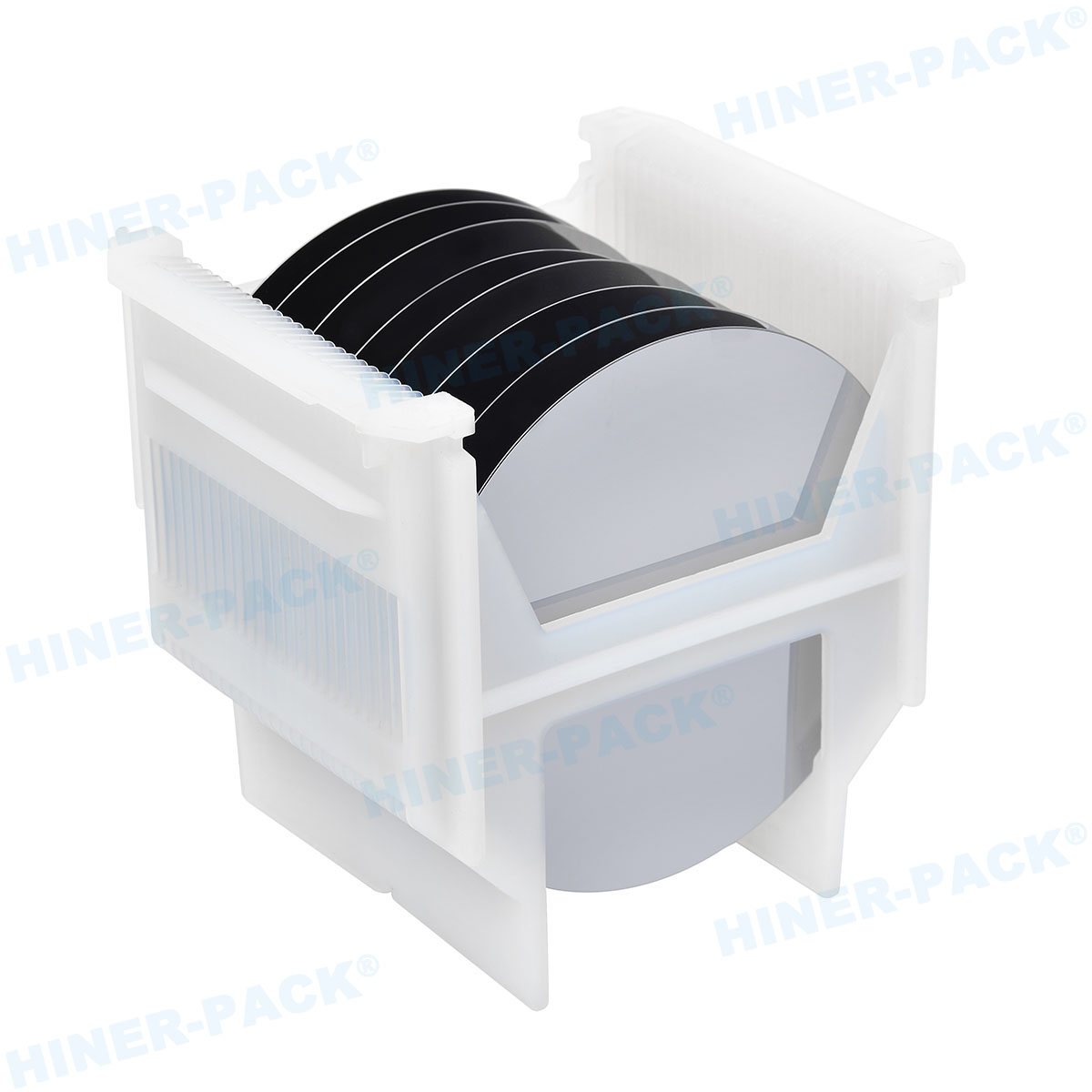
In semiconductor manufacturing, handling fragile dies trays is a fundamental aspect that directly impacts product quality and yield. These trays hold delicate silicon dies during processes like testing, sorting, and transportation. Any mishandling can lead to costly damage, defects, or complete loss. This article explores practical approaches to ensure safe and efficient management of these critical components.

The Importance of Proper Handling for Fragile Dies Trays
Effective handling fragile dies trays is vital for maintaining the integrity of semiconductor devices. As dies become smaller and more complex, their susceptibility to physical stress increases. Proper handling minimizes risks and supports high production standards.
Why Fragility Matters in Semiconductor Dies
Modern semiconductor dies are thin and sensitive. They can easily crack or suffer electrostatic discharge (ESD) damage. Trays must provide secure cushioning and protection throughout the supply chain.
Key factors include:
Die thickness and material composition.
Environmental exposure to moisture or contaminants.
Mechanical shocks during movement.
Risks of Improper Handling
Neglecting proper procedures can result in significant losses. Common issues include die breakage, surface scratches, and alignment errors. These problems lead to reduced yield and higher operational costs.
Financial losses from scrapped materials.
Delays in production timelines.
Compromised device reliability.
Key Challenges in Handling Fragile Dies Trays
Managing handling fragile dies trays involves overcoming various obstacles. From environmental conditions to human factors, each challenge requires targeted solutions to prevent damage.
Environmental Factors
Cleanrooms and controlled settings are essential. Temperature fluctuations, humidity, and particulate contamination can affect tray stability. Consistent monitoring is necessary to maintain optimal conditions.
Considerations:
Maintaining low humidity to prevent corrosion.
Using HEPA filters to reduce dust.
Stable temperatures to avoid material expansion.
Human Error Considerations
Manual handling introduces risks like drops or misalignment. Training and automation can mitigate these errors. Standardized protocols ensure that operators follow safe practices consistently.
Implementing clear handling guidelines.
Regular skill assessments for staff.
Using ergonomic tools to reduce fatigue.
Best Practices for Handling Fragile Dies Trays
Adopting robust methods for handling fragile dies trays enhances protection and efficiency. These practices cover equipment use, procedural steps, and quality checks.
Using the Right Equipment
Specialized tools are crucial. Vacuum wands, tweezers, and automated handlers reduce direct contact. Trays should meet JEDEC standards for compatibility and safety.
Recommended equipment:
ESD-safe trays and containers.
Precision robotic arms for automation.
Anti-static mats and grounding straps.
Training and Protocols
Comprehensive training programs educate workers on proper techniques. Protocols should include step-by-step instructions for loading, unloading, and transporting trays.
Simulation exercises for hands-on learning.
Documentation of handling procedures.
Regular audits to ensure compliance.
Tools and Solutions from Hiner-pack
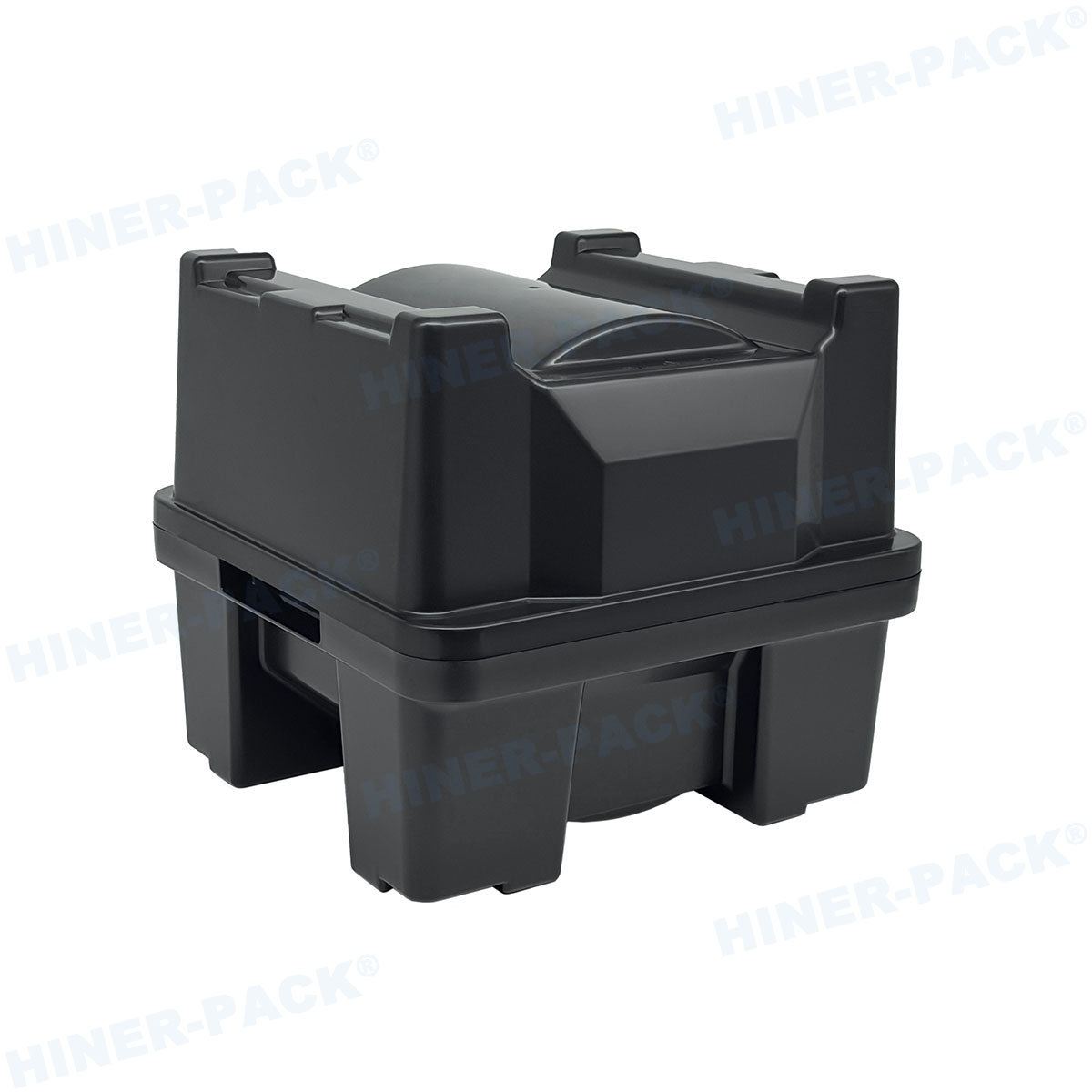
Hiner-pack offers advanced solutions for handling fragile dies trays. Their products are designed to meet the stringent demands of the semiconductor industry, providing reliability and innovation.
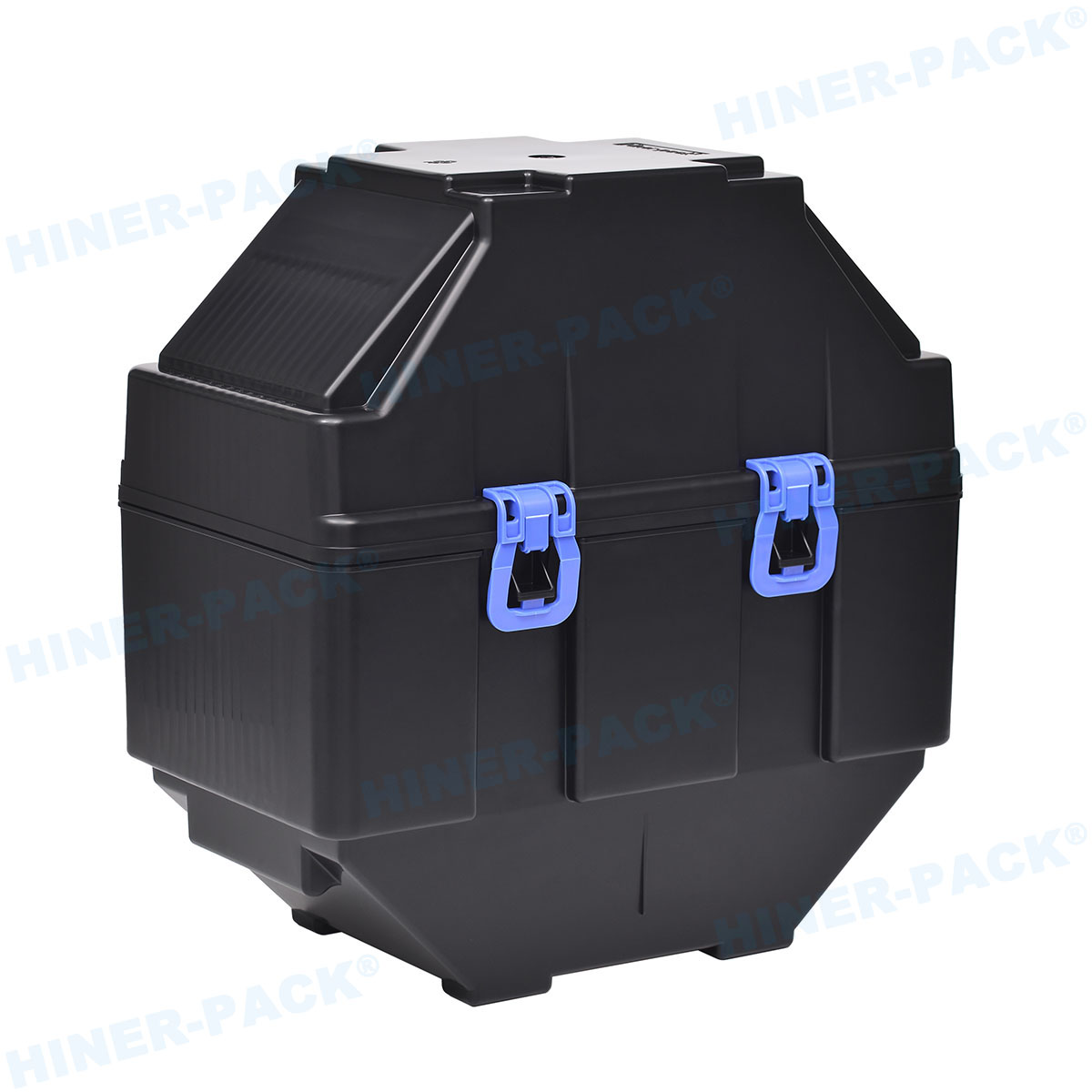
Innovative Trays and Containers
Hiner-pack develops trays with enhanced materials for better protection. Features include shock-absorbing designs and anti-static properties. These trays support safe storage and transportation.
Customizable sizes for various die dimensions.
High-temperature resistance for processing stages.
Stackable designs to save space.
How Hiner-pack Enhances Safety
By integrating quality controls and user-focused designs, Hiner-pack reduces handling risks. Their trays are tested for durability and compatibility with automated systems.
Benefits:

Future Trends in Dies Tray Handling
The evolution of handling fragile dies trays is shaped by technological advancements. Automation and smart materials are paving the way for more resilient processes.
Automation and Robotics
Robotic systems are becoming standard in fabs. They offer precision and reduce human intervention. Vision systems assist in accurate placement and inspection.
AI-driven error detection.
Collaborative robots for flexible operations.
Integration with IoT for real-time monitoring.
Material Advancements
New polymers and composites are being developed for trays. These materials provide better protection against physical and environmental stresses. Research focuses on sustainability and reusability.
Biodegradable options for eco-friendly disposal.
Enhanced ESD shielding properties.
Lightweight designs for easier handling.
Conclusion
In summary, handling fragile dies trays is a critical component of semiconductor manufacturing. By implementing best practices, leveraging tools from companies like Hiner-pack, and staying updated with trends, industries can safeguard their products and boost efficiency. Proper management ensures that delicate dies remain intact from fabrication to end-use.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What are the primary risks when handling fragile dies trays?
A1: The main risks include physical damage such as cracks or chips, electrostatic discharge (ESD) that can destroy electronic components, and contamination from dust or moisture. These issues can lead to yield loss and increased costs.
Q2: How can automation improve the handling of fragile dies trays?
A2: Automation reduces human error by using robotic systems for precise movement. It ensures consistent speed and alignment, minimizes direct contact, and can integrate with sensors for real-time quality checks.
Q3: What standards should dies trays comply with for safe handling?
A3: Trays should adhere to JEDEC standards for dimensions and materials. They often need ESD protection (e.g., ANSI/ESD S20.20), and compatibility with industry equipment like pick-and-place machines.
Q4: Why is training important for personnel handling fragile dies trays?
A4: Training ensures that operators understand proper techniques, such as using ESD-safe tools and following protocols. It reduces accidents, improves efficiency, and maintains a culture of safety in the workplace.
Q5: How does Hiner-pack contribute to better handling of fragile dies trays?
A5: Hiner-pack designs specialized trays with features like shock absorption and anti-static properties. Their solutions are tested for durability and help streamline processes, offering reliable protection for semiconductor dies.