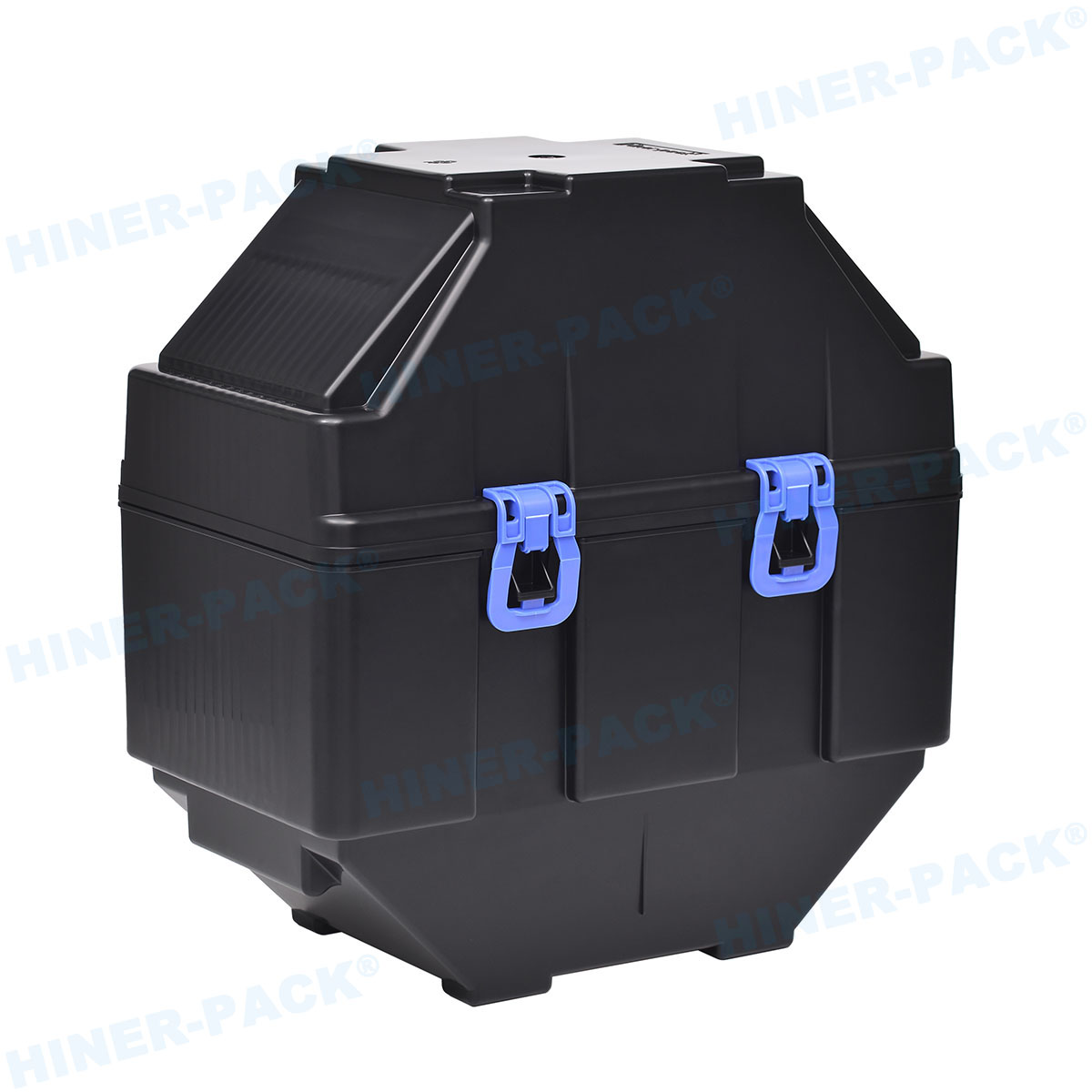
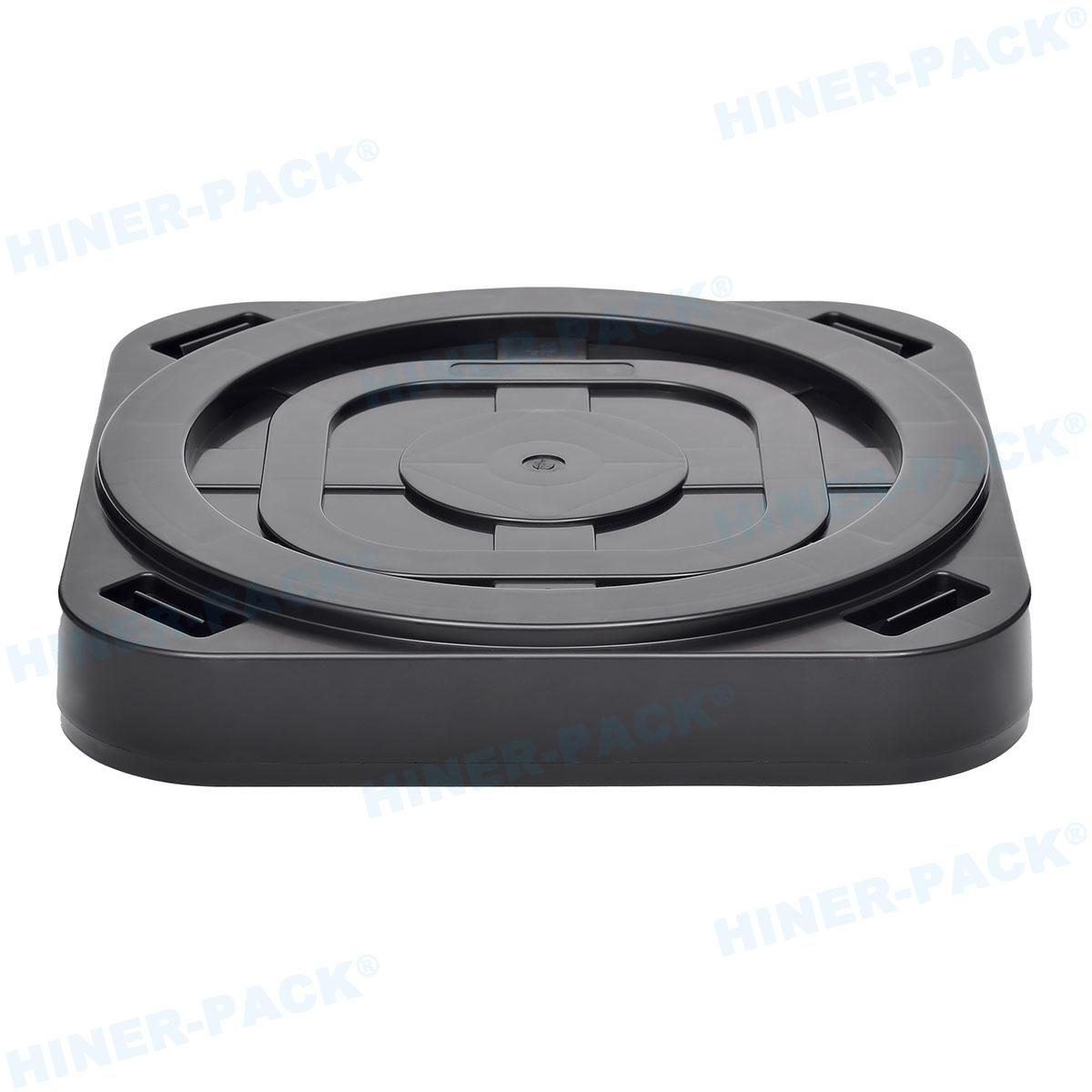
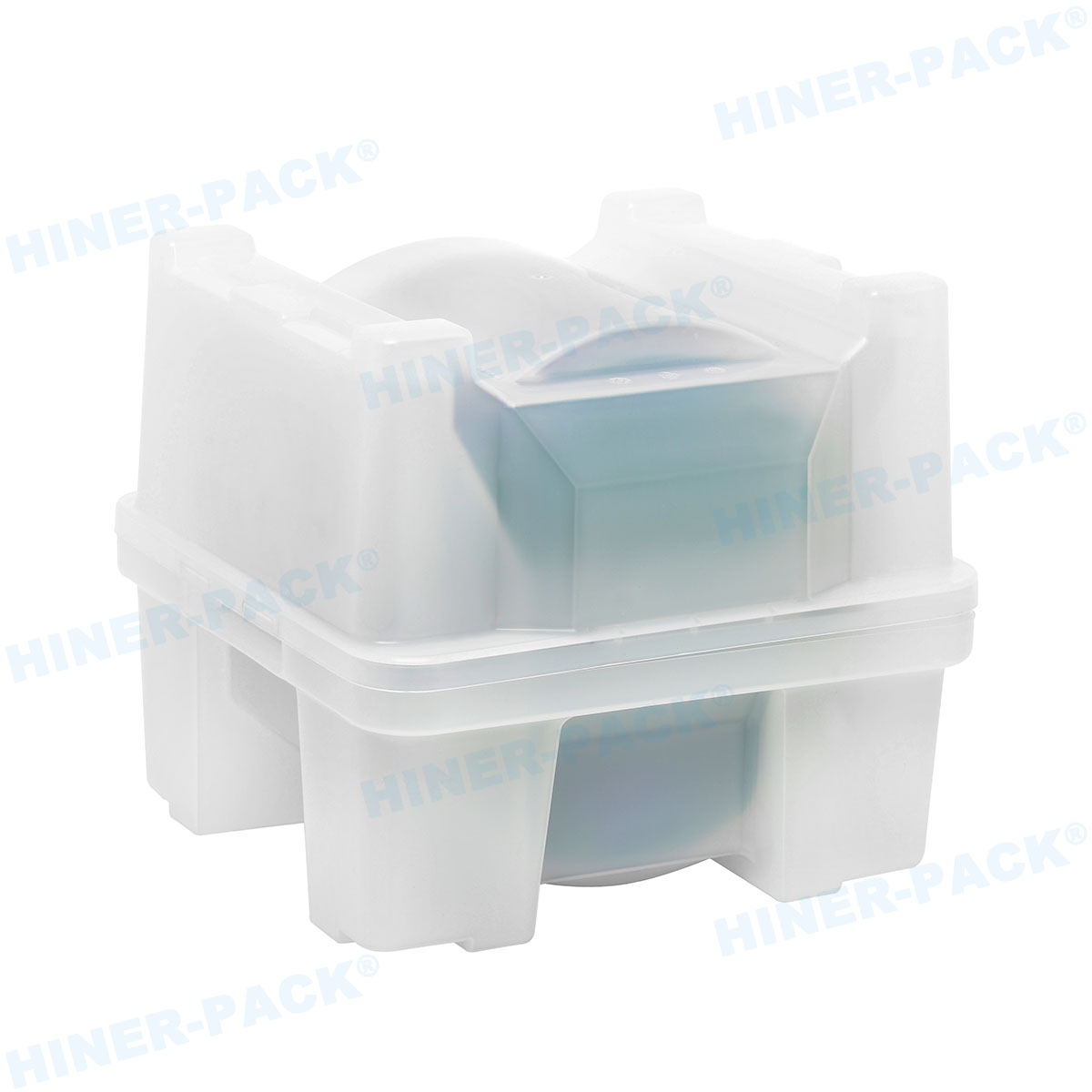
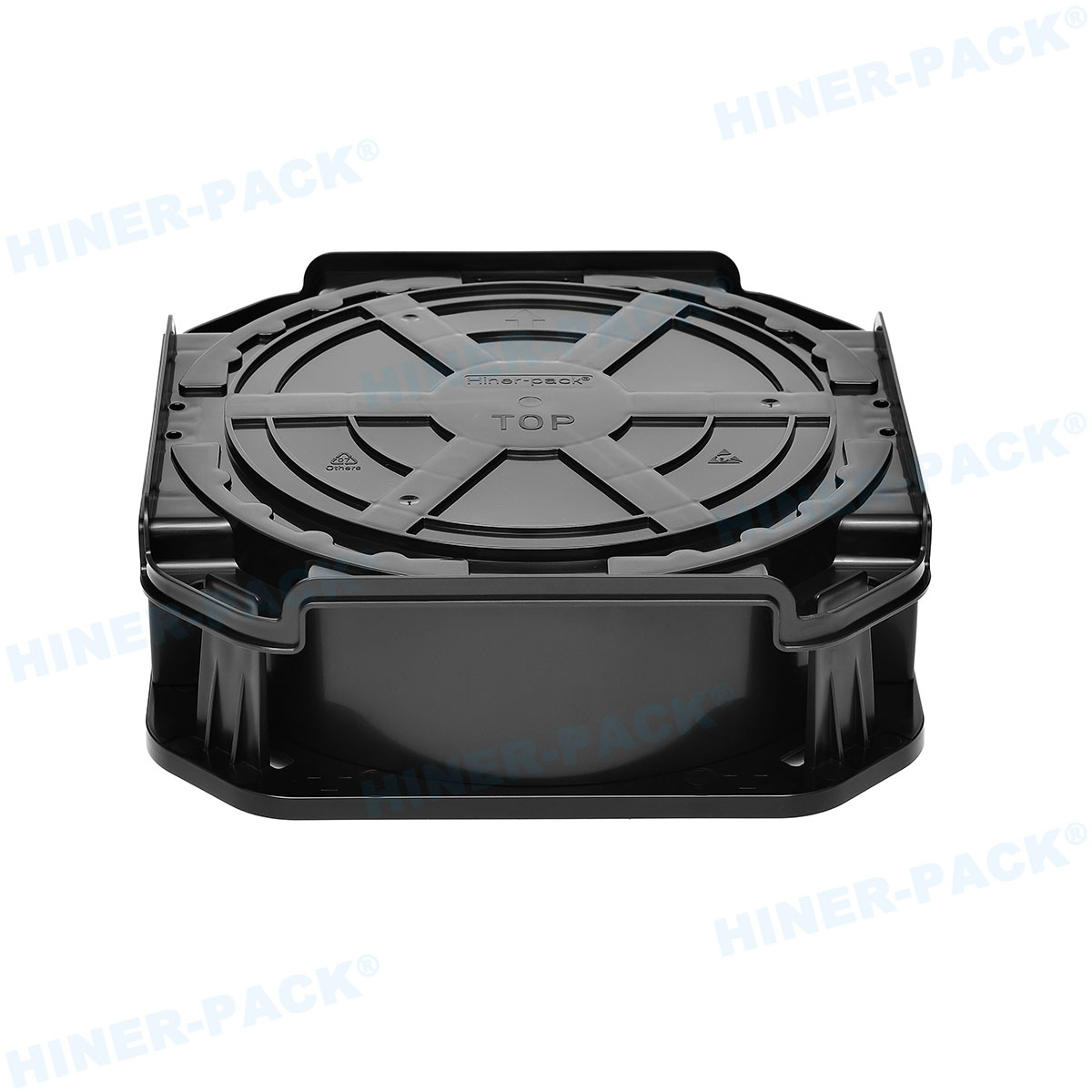
In the fast-paced world of semiconductor manufacturing and testing, consistency is the foundation of efficiency. When components move between fabrication, assembly, test, and shipment, even minor discrepancies in handling can cause delays, damage, and cost overruns. This is where the universal language of hardware, defined by JEDEC standard trays, proves indispensable. These standardized carriers provide a predictable, reliable interface for delicate integrated circuits and other components throughout their production journey.
For engineers and supply chain managers, specifying a JEDEC standard tray means eliminating guesswork. It ensures that a device package will fit securely, that automation equipment will engage correctly, and that trays from one supplier will stack neatly with those from another. This interoperability is critical for lean operations.
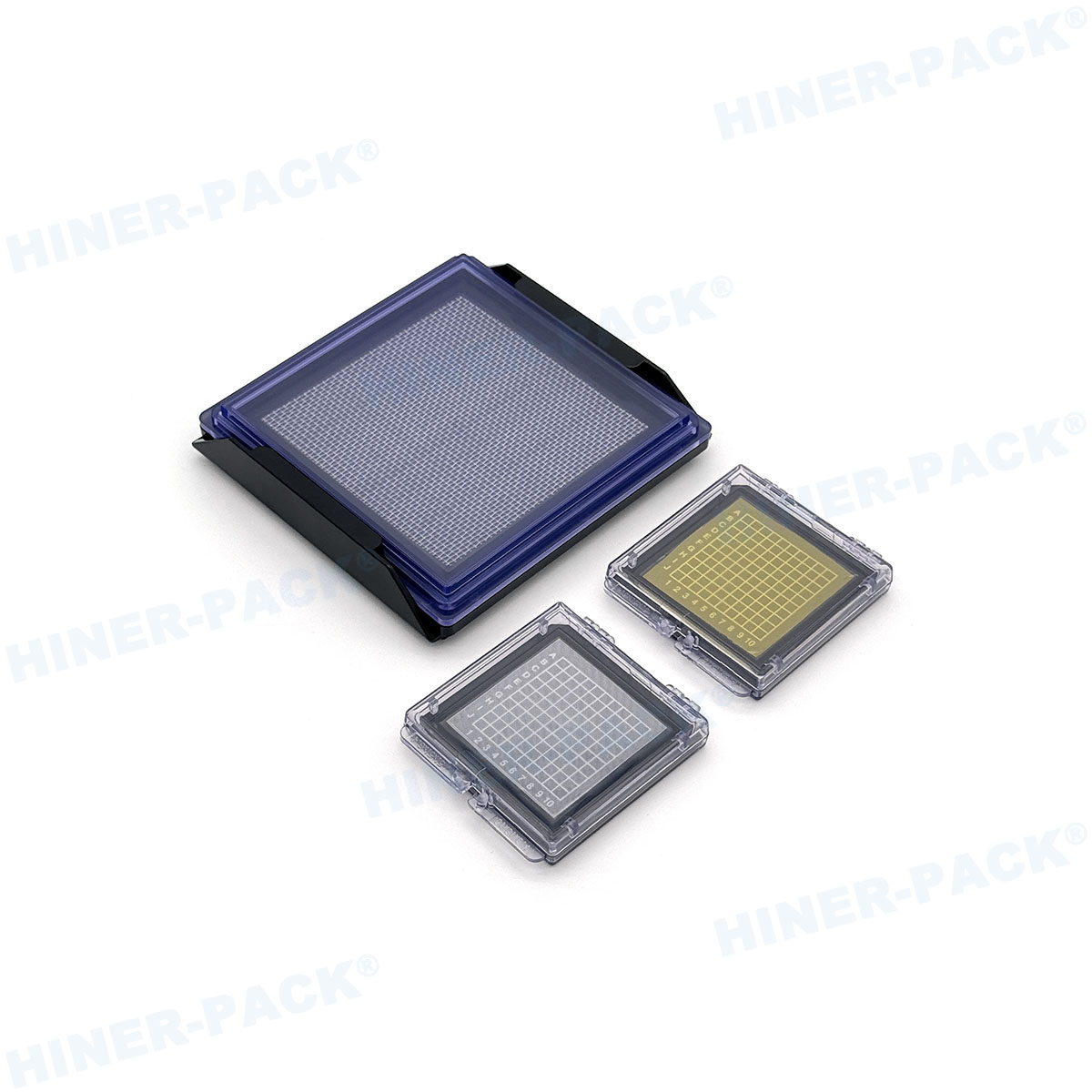

What Are JEDEC Standards and Why Do They Matter?
JEDEC Solid State Technology Association is the global leader in developing open standards for the microelectronics industry. Its publications cover everything from device specifications to quality guidelines and, crucially, mechanical standards for carriers.
These standards provide precise dimensional and material specifications for trays, tubes, and other handling media. By adhering to these published guidelines, manufacturers of carriers, like Hiner-pack, and users of those carriers create a plug-and-play ecosystem. This eliminates the need for custom fixtures for every new device or production line, saving significant time and capital expenditure.
The Critical Role of Standardized Trays in the Supply Chain
The journey of a semiconductor device is long and complex. After assembly, devices may be shipped to a test facility, then to a distributor, and finally to the electronics manufacturer. At each hand-off point, devices are transferred between handling media.
Without standardization, this process would be chaotic. Custom trays might not fit into another company’s automation rack or tester socket. JEDEC standard trays act as universal translators. They ensure that a tray of microcontrollers from a facility in Asia can be seamlessly unloaded by a surface-mount technology (SMT) placement machine at a contract manufacturer in Europe. This smooths logistics and reduces handling, which directly lowers the risk of physical damage like bent leads or cracked packages.
Key Design Features of JEDEC-Compliant Trays
The design of these trays is a study in practical engineering. Every feature serves a specific purpose for protection, handling, and automation.
The cavity geometry is precisely defined to cradle the device package without pinching or allowing excessive movement. Materials are carefully selected. Common choices include static-dissipative polycarbonate or advanced polymer blends like PEEK for high-temperature processes. These materials prevent electrostatic discharge (ESD) damage, withstand repeated wash cycles, and offer the right balance of rigidity and impact resistance.
Robust stacking features are another hallmark. Interlocking lugs and ribs ensure stable, vertical stacking during storage and transport, preventing tower collapse. Clear, machine-readable labels and areas for barcodes are also integral, supporting track-and-trace systems throughout the supply chain.
Common JEDEC Tray Standards and Their Applications
Several key JEDEC standards define trays for different package families. Understanding these helps in selecting the right carrier.
The JESD30 series is fundamental, covering outline dimensions for various package types like quad flat packs (QFPs) and thin quad flat packs (TQFPs). The widely referenced JEDEC Standard Tray, often specified for a range of package sizes, is defined under these guidelines.
For smaller, high-volume packages like ball grid arrays (BGAs) and chip-scale packages (CSPs), standards like those outlined in JEP95 provide detailed mechanical drawings for matrix trays. These trays hold dozens or hundreds of devices in a precise grid, optimized for automated pick-and-place operations. Hiner-pack’s production line includes a comprehensive range of trays compliant with these critical specifications, ensuring reliable performance for modern, miniaturized components.
Quality and Compliance: More Than Just Dimensions
True compliance goes beyond simply matching length and width. Reputable manufacturers build quality into every step. This involves rigorous testing for key performance indicators.
Trays must be tested for ESD resistance, ensuring they meet the required surface resistivity and discharge thresholds. Dimensional stability is verified under various temperature and humidity conditions to simulate real-world environments. Mechanical life cycling tests confirm that stacking features and tray bodies won’t warp or fail after hundreds of uses.
Hiner-pack invests in this level of validation. Their quality assurance processes ensure that every batch of JEDEC standard trays not only meets the printed spec but also performs reliably under the stress of daily industrial use.
The Economic Advantage of Using Certified Trays
While off-spec or generic trays might have a lower upfront cost, they carry hidden risks and expenses. Incompatibility can halt an SMT line, causing thousands of dollars in downtime per hour. Poor material quality can lead to particle contamination or ESD events, resulting in field failures.
Investing in certified trays from a trusted supplier mitigates these risks. It ensures maximum compatibility with global equipment and processes, reduces the likelihood of handling damage, and extends the usable life of the tray through durable materials and construction. This results in a lower total cost of ownership and greater peace of mind.
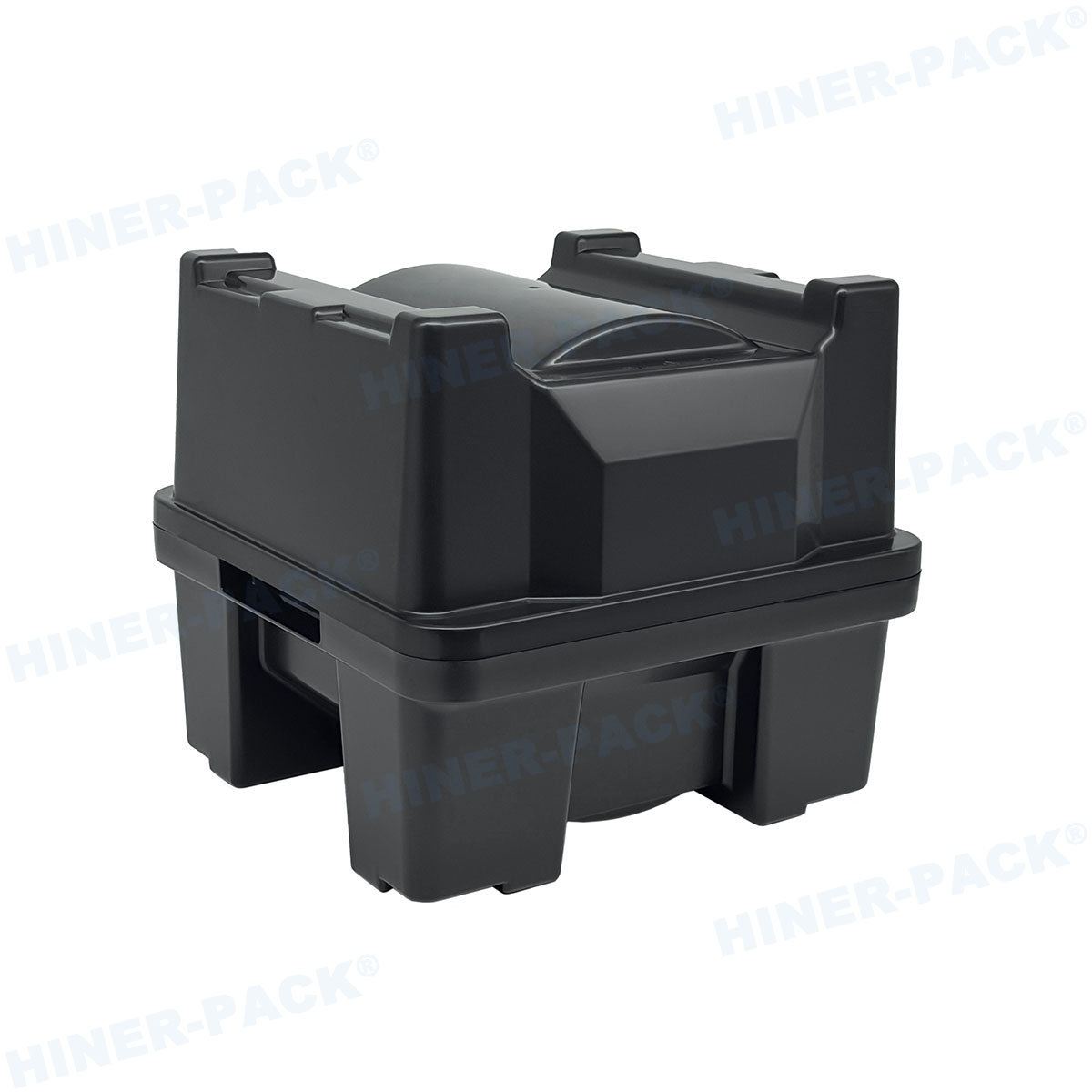

Hiner-pack's Commitment to Precision and Reliability
As a specialist in semiconductor handling solutions, Hiner-pack’s philosophy aligns perfectly with the mission of JEDEC standards: to enable interoperability and reliability. Their engineering team deeply understands the nuances of each published standard.
They focus on precision molding to achieve the exact cavity tolerances required for secure device retention. Material selection is a science, choosing the right polymer compound for the application, whether it needs superior chemical resistance for cleaning or high thermal stability for burn-in processes. By manufacturing trays that are faithfully compliant, Hiner-pack provides customers with a seamless, worry-free link in their production chain.
Conclusion: The Unseen Backbone of Electronics Manufacturing
In an industry defined by microscopic transistors and gigahertz speeds, the humble tray plays an outsize role. JEDEC standard trays are the unsung heroes of semiconductor logistics. They provide the mechanical foundation that allows for automated, efficient, and safe handling of valuable components on a global scale.
By specifying and using trays that adhere strictly to these industry standards, companies protect their investment in silicon, optimize their manufacturing flow, and build a more resilient supply chain. Partners like Hiner-pack, through their commitment to precision and quality, ensure that this foundational element performs its critical duty, shipment after shipment.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: How does a JEDEC tray standard relate to a specific JESD publication?
A1: A JEDEC tray standard is typically published as part of the JESD (JEDEC Solid State) series of documents. For example, the mechanical outline for a particular package tray will be detailed in a JESD standard like JESD30 or within a specific package family standard in the JEP95 series. The publication provides all necessary dimensional drawings, material requirements, and test guidelines.
Q2: Are JEDEC trays only for shipping, or are they used in production too?
A2: They are used extensively throughout production. Their primary role is in automation. They are designed to interface directly with automated test equipment (ATE) handlers, vision inspection systems, and SMT pick-and-place machines. Their standardized dimensions are crucial for this automated hand-off, making them essential for in-facility material handling as much as for inter-facility shipping.
Q3: What is the difference between a matrix tray and a cavity tray in JEDEC standards?
A3: A cavity tray has individual, separated pockets (cavities) for each device, common for larger packages like QFPs. A matrix tray holds many smaller devices (like BGAs) in a contiguous grid pattern, with dividers forming the matrix. The choice depends on the package type, volume, and the need for individual device isolation versus high-density storage.
Q4: Can Hiner-pack provide trays that are compliant with both JEDEC and customer-specific requirements?
A4: Yes. While Hiner-pack specializes in fully compliant off-the-shelf JEDEC standard trays, they also offer customization. This can include adding specific logos, modifying color for product differentiation, or incorporating minor design adaptations—such as special fiducials or RFID tags—while maintaining core compliance dimensions to ensure equipment compatibility.
Q5: How should JEDEC trays be maintained and cleaned for long-term use?
A5: Proper maintenance is key. Use approved cleaners (like deionized water or specific solvents) that won’t degrade the static-dissipative properties or cause stress cracking. Avoid high-pressure sprays that can damage delicate features. Store trays in stable, moderate environments to prevent warping. Regularly inspect for physical damage, particulate accumulation, or worn stacking features, and remove damaged trays from circulation immediately.