JEDEC Trays for Automotive ICs: Standards, Materials, and Handling GuideThe reliability of automotive integrated circuits (ICs) begins with how they are handled and transported. Using the correct JEDEC trays for automotive ICs is a fundamental requirement in the semiconductor supply chain. These trays protect sensitive components from damage, contamination, and electrostatic discharge throughout manufacturing and assembly.
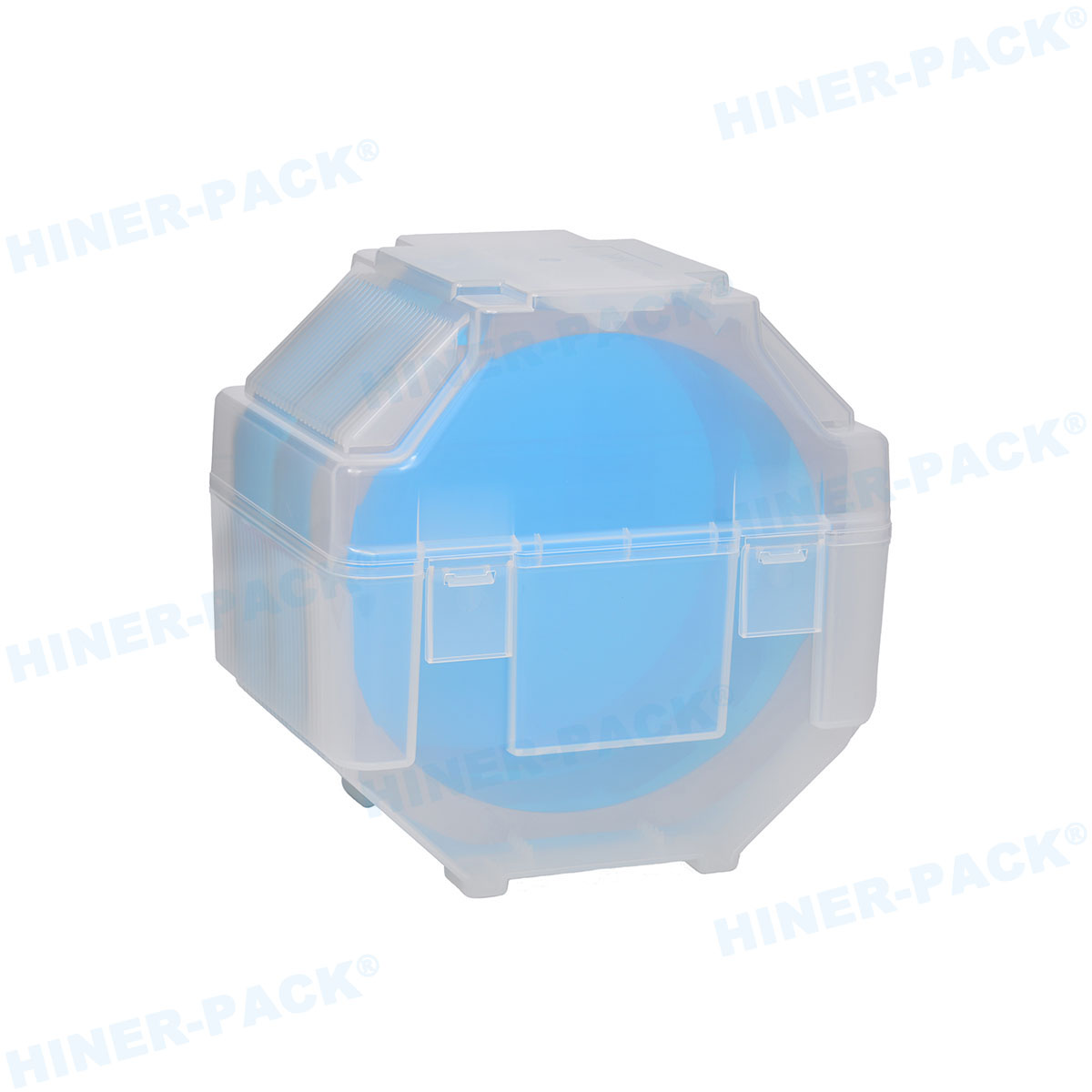

Why JEDEC Trays Are Critical for Automotive Semiconductor Packaging
Automotive electronics operate in harsh environments. Components must withstand extreme temperatures, vibration, and humidity. The packaging used during transit and storage plays a direct role in final product reliability.
JEDEC trays for automotive ICs provide a standardized, secure housing. They prevent physical damage like bent leads or cracked packages. This is vital for zero-defect goals in the automotive industry.
Key reasons for their importance:
Ensuring component integrity from test to board assembly.
Enabling automation in pick-and-place and handling systems.
Maintaining traceability through standardized dimensions.
Protecting against environmental and electrostatic hazards.
Understanding JEDEC Standards: A Foundation for Interoperability
JEDEC (Joint Electron Device Engineering Council) creates global standards for the semiconductor industry. Tray standards ensure compatibility across different manufacturers and assembly lines.
Key JEDEC Tray Standards for Automotive Components
Several standards define tray dimensions, materials, and handling features. Common standards include JESD30 (for matrix trays) and JESD609 (for handling and shipping).
Adherence to these standards guarantees that trays will fit automated equipment. It eliminates compatibility issues between suppliers and OEMs.
Matrix Trays (JESD30): Define pocket layout, pitch, and overall tray size.
Thermal and Mechanical Specifications: Outline material properties and temperature resistance.
ESD Standards: Specify requirements for electrostatic discharge protection.
Stacking and Interlocking Features: Ensure safe stacking during storage and transport.
Material Selection for Harsh Automotive Environments
The material of a JEDEC tray determines its performance. Automotive applications demand materials that can endure rigorous conditions.
Common materials include conductive and static-dissipative compounds. These materials protect ICs from electrostatic damage during handling.
Material considerations include:
High-Temperature Plastics: Materials like PEEK or high-temp PCT can withstand reflow and baking processes.
ESD-Safe Properties: Carbon-loaded or permanent static-dissipative plastics prevent charge buildup.
Dimensional Stability: The tray must not warp under temperature cycling or humidity changes.
Chemical Resistance: Protection against cleaning agents or fluxes used in assembly.
Suppliers like Hiner-pack provide trays engineered with these automotive-grade materials.
Design Features for Safe Handling and Automation
The physical design of a tray supports efficient and damage-free handling. This is crucial in high-volume automotive IC production.
Design features focus on automation compatibility and component security. They enable robots and machinery to reliably insert and extract components.
Important design aspects:
Precision-Molded Pockets: Securely hold ICs without applying stress to leads or balls.
Tooling Holes and Notches: Allow for precise alignment on conveyor belts and machine platforms.
Stacking Ribs and Interlocks: Prevent trays from sliding or crushing components when stacked.
Identification Areas: Flat surfaces for barcode or RFID labels to track lot numbers.
Quality and Reliability Testing for Automotive Compliance
Automotive components must meet stringent quality standards like AEC-Q100. The trays that carry them must also pass rigorous tests.
Testing ensures trays perform reliably over time and under stress. This prevents tray failure from causing component damage.
Typical test protocols for JEDEC trays for automotive ICs include:
Thermal Cycling: Exposing trays to repeated high and low temperatures.
ESD Performance Verification: Measuring surface resistivity and charge decay.
Mechanical Durability: Testing for warpage, cracking, and pocket integrity after repeated use.
Cleanliness Testing: Ensuring trays do not outgas or generate particles that contaminate ICs.
The Role in the Automotive Supply Chain and Logistics
From semiconductor fab to tier-1 supplier, JEDEC trays provide a consistent handling medium. They are part of a controlled logistics process.
Trays move components through testing, shipping, and surface-mount technology (SMT) lines. Standardization reduces touch points and handling errors.
Supply chain benefits:
Simplifies inventory management with standardized footprints.
Reduces packaging waste compared to disposable alternatives.
Facilitates return and reuse loops for cost efficiency.
Enables just-in-time delivery by fitting automated warehouse systems.
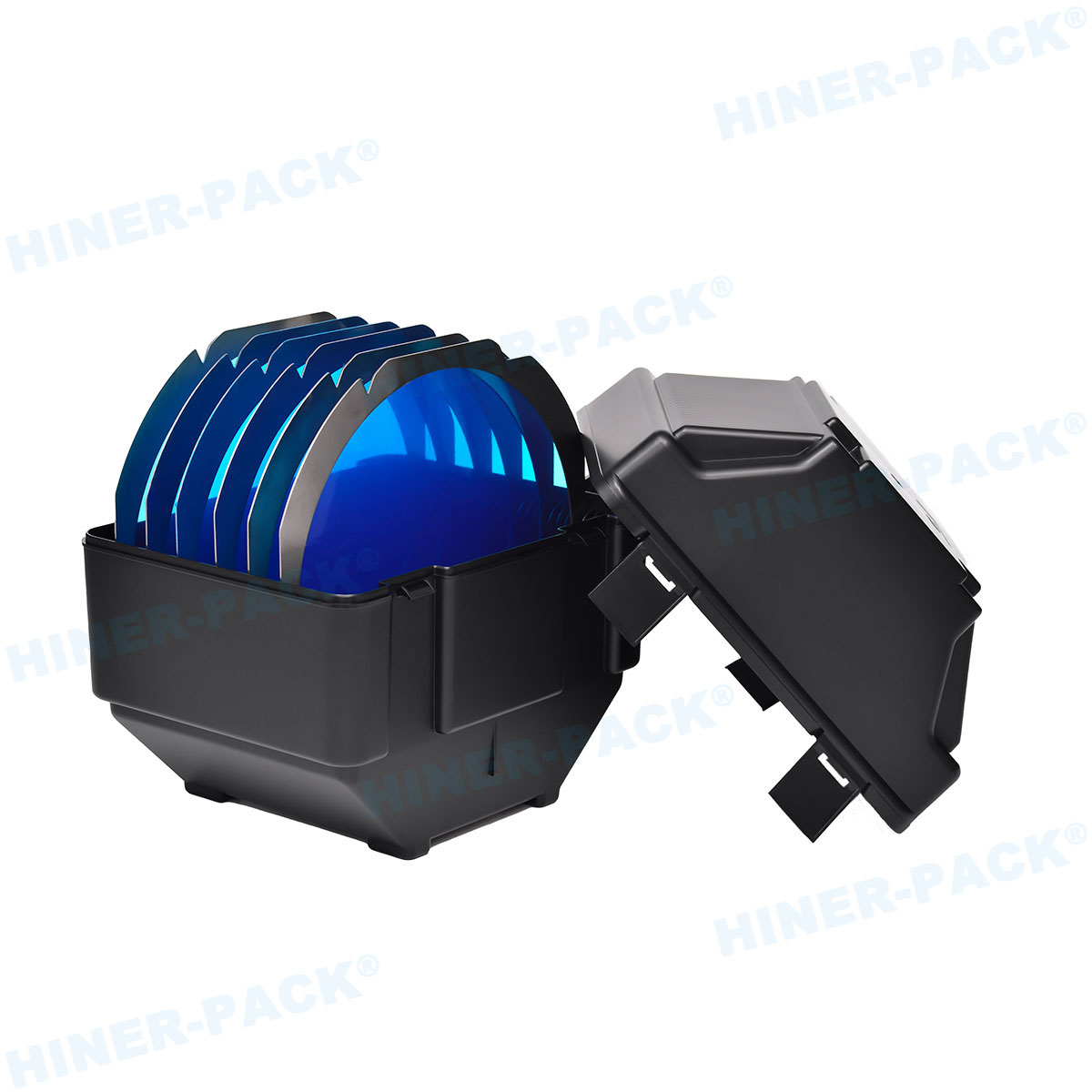

Selecting the Right Supplier: Key Considerations
Choosing a supplier for JEDEC trays requires careful evaluation. The supplier must understand automotive industry demands.
Factors include material expertise, quality systems, and ability to meet volume requirements. Technical support for customization is also valuable.
Selection criteria:
Certifications: Compliance with ISO 9001 and IATF 16949 quality standards.
Material Traceability: Full documentation of material sources and properties.
Proven Experience: Track record supplying to automotive semiconductor companies.
Customization Capability: Ability to design trays for non-standard or new package types.
Hiner-pack specializes in providing robust JEDEC trays for automotive ICs, meeting these stringent requirements.
Best Practices for Handling and Maintenance
Proper handling extends tray life and protects components. Establishing clear procedures is essential for factory personnel.
Trays should be handled in ESD-safe areas. Regular inspection and cleaning prevent contamination and damage.
Recommended practices:
Store trays in controlled environments away from direct sunlight and moisture.
Use automated handling equipment where possible to minimize manual contact.
Implement a regular cleaning schedule using approved methods and materials.
Inspect trays for wear, cracks, or pocket deformation before each reuse cycle.
In the automotive semiconductor industry, there is no room for packaging failure. The use of properly specified and manufactured JEDEC trays for automotive ICs is a critical control point. It ensures component quality, supports automated manufacturing, and upholds the reliability standards demanded by modern vehicles. Partnering with a knowledgeable supplier like Hiner-pack provides access to trays that meet the exacting standards of this vital sector.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What is the main difference between a JEDEC tray and other IC trays?
A1: JEDEC trays are built to specific industry-wide standards (like JESD30) ensuring dimensional interoperability across all suppliers and equipment. Generic trays may not guarantee this fit, risking handling issues.
Q2: Are all JEDEC trays suitable for automotive-grade components?
A2: Not automatically. Trays for automotive ICs often require specific high-temperature, high-reliability materials and stricter ESD protection. They must be explicitly designed and tested for automotive supply chain conditions.
Q3: How do I know which JEDEC tray standard applies to my automotive IC package?
A3: The package outline (e.g., QFP, BGA) and its dimensions dictate the correct tray standard. Consult the JEDEC publication or work with your tray supplier to match the package to the appropriate JESD tray outline.
Q4: Can JEDEC trays be reused, and for how long?
A4: Yes, high-quality trays are designed for multiple reuse cycles. Their lifespan depends on the material, handling care, and the environment. Regular inspection is needed to retire trays showing wear, warpage, or contamination.
Q5: Why is ESD protection so critical in trays for automotive ICs?
A5: Automotive ICs often use advanced process nodes sensitive to electrostatic discharge. ESD damage can cause latent failures, reducing the long-term reliability of the electronic control unit in a vehicle.
Q6: Does Hiner-pack offer custom JEDEC tray solutions for new package types?
A6: Yes. Hiner-pack provides engineering support to develop custom or modified JEDEC-compliant trays for new or proprietary automotive IC packages, ensuring they meet all handling and reliability requirements.