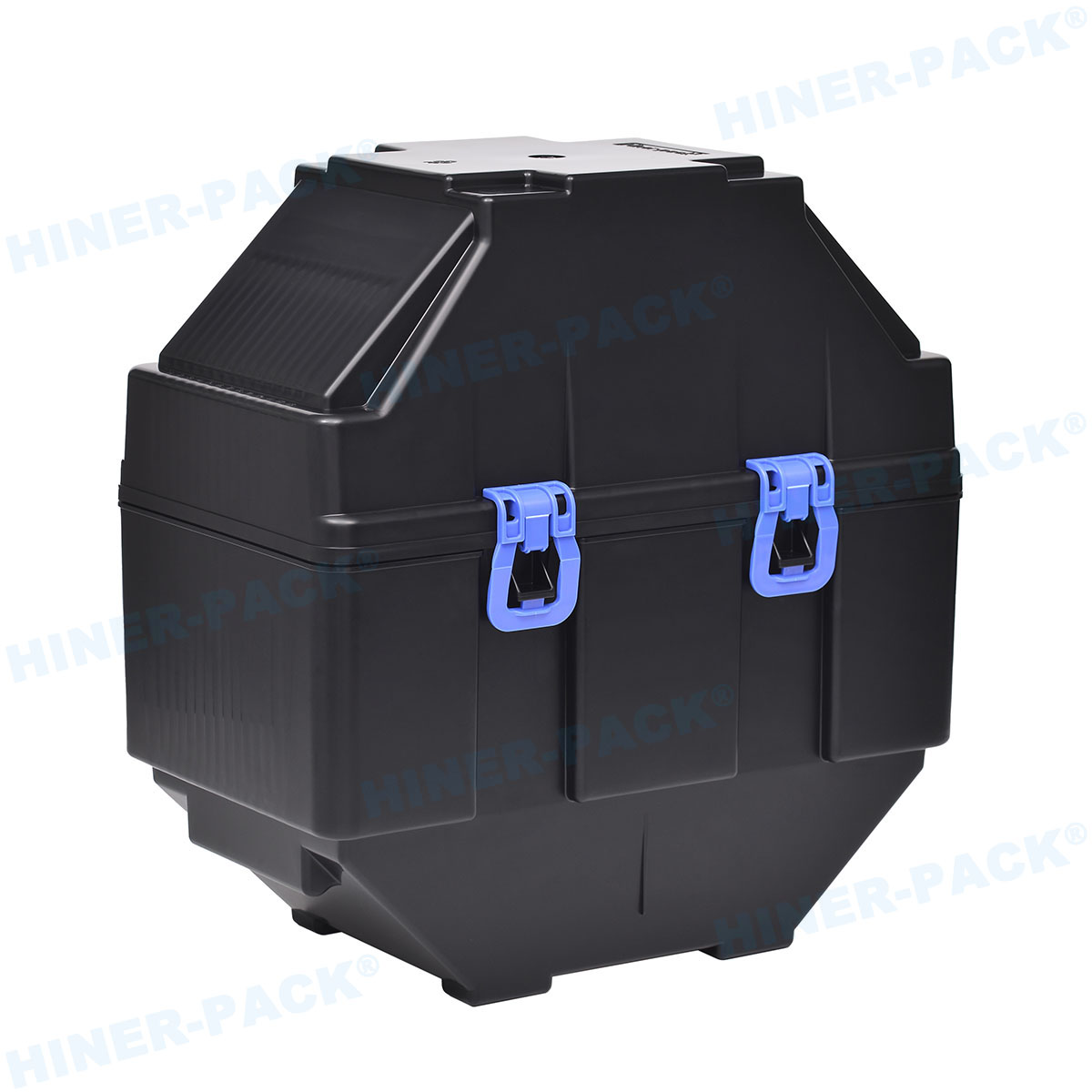
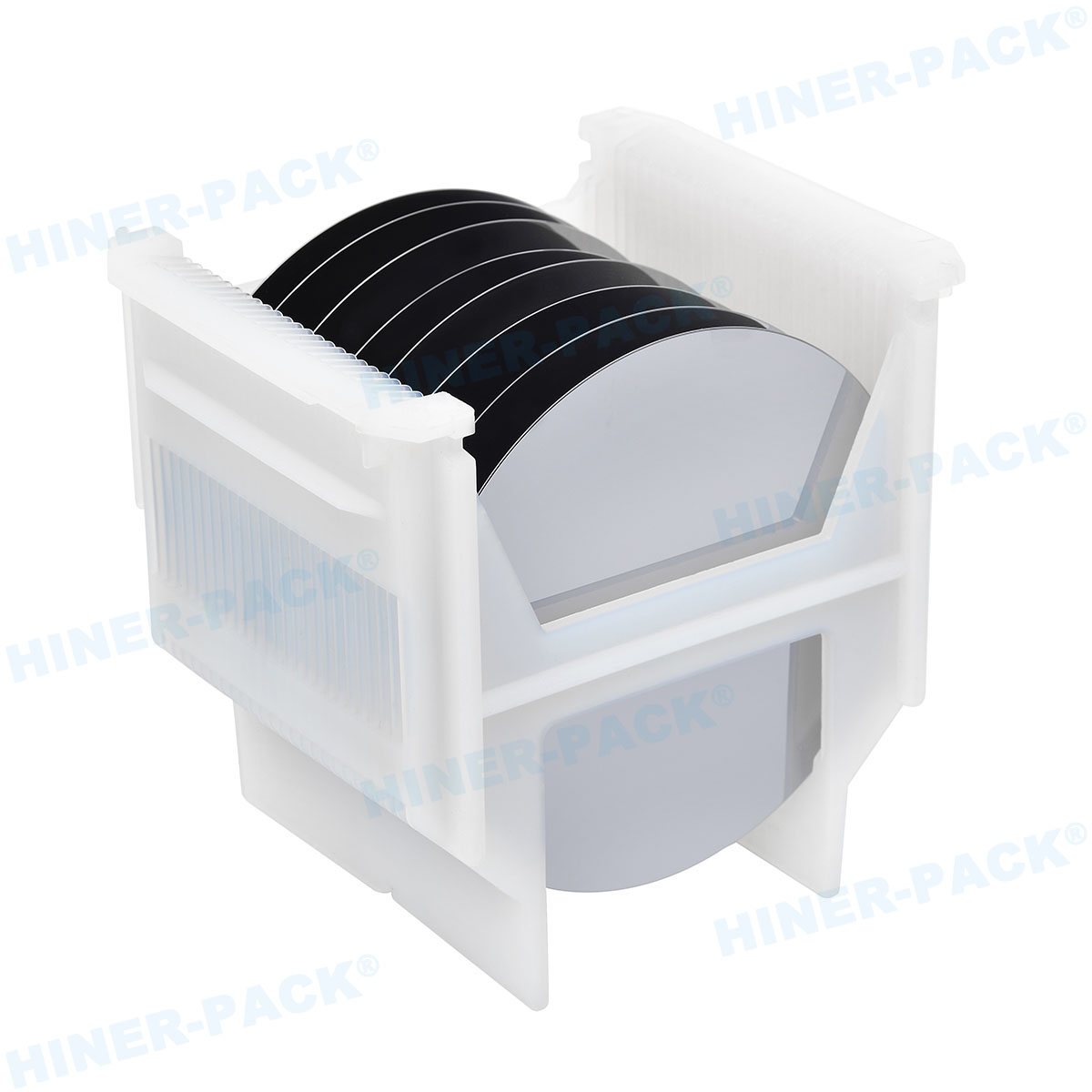
Wafer Carrier for Fab Plant: Types, Functions, and Selection GuideIn semiconductor manufacturing, protecting silicon wafers is critical for high yield and quality. A wafer carrier for fab plant serves as a specialized container to safeguard wafers during processing, storage, and transport. This article explains the key aspects of wafer carriers, from design to application, helping professionals make informed decisions.

Introduction to Wafer Carriers in Semiconductor Fabs
Semiconductor fabrication plants (fabs) rely on precise handling systems. Wafer carriers are essential tools that hold wafers securely. They prevent contamination, damage, and loss throughout production.
These carriers support automation and cleanliness. They are designed to meet strict industry standards. Proper use of a wafer carrier for fab plant improves operational efficiency.
Key benefits include:
Reduced particle contamination on wafer surfaces.
Enhanced safety during robotic handling.
Compatibility with various fab equipment and processes.
Improved traceability and inventory management.
Types of Wafer Carriers for Fab Plants
Different wafer carriers are used based on wafer size and fab requirements. Common types include FOUPs, FOSBs, and SMIF pods.
Front Opening Unified Pod (FOUP)
FOUPs are standard for 300mm wafer processing. They feature a front-opening door that seals tightly. This design minimizes exposure to ambient air.
FOUPs integrate with tool load ports. They support high-volume manufacturing in advanced fabs.
Materials: Often made from polycarbonate or PEEK.
Capacity: Typically holds 13 to 25 wafers.
Applications: Used in etching, deposition, and lithography steps.
Front Opening Shipping Box (FOSB)
FOSBs are similar to FOUPs but designed for shipping. They protect wafers during inter-facility transport. FOSBs include additional padding and sealing.
They ensure wafers remain clean and undamaged. FOSBs are crucial for supply chain logistics.
Standard Mechanical Interface (SMIF) Pods
SMIF pods are used for 200mm and smaller wafers. They provide a controlled mini-environment. Robotic arms handle these pods automatically.
SMIF systems reduce manual intervention. They are common in older fab lines still in operation.
Key Functions of a Wafer Carrier for Fab Plant
The primary role of a wafer carrier for fab plant is to ensure wafer integrity. It acts as a protective shell during fab operations.
Carriers facilitate smooth movement between tools. They help maintain a cleanroom environment. This reduces defect rates and improves yield.
Specific functions include:
Shielding wafers from dust, moisture, and static electricity.
Preventing physical damage like scratches or breaks.
Enabling automated transport via overhead hoists or robots.
Providing identification through barcodes or RFID tags.
Design and Material Considerations
Wafer carriers must balance durability and cleanliness. Material selection impacts performance and longevity.
Common materials include polycarbonate, PEEK, and stainless steel. Each offers unique advantages for fab conditions.
Polycarbonate: Lightweight and cost-effective for general use.
PEEK: Resists high temperatures and harsh chemicals.
Stainless Steel: Used for structural parts to enhance strength.
Design focuses on minimizing particle generation. Smooth surfaces and tight tolerances are critical. Carriers must also dissipate static charge to protect sensitive wafers.
Integration with Fab Automation Systems
Modern fabs use automation to boost productivity. Wafer carriers must work seamlessly with robotic systems.
They interface with equipment load ports and conveyors. Standards like SEMI E15 and E19 ensure compatibility.
Automation benefits include:
Faster wafer handling and reduced cycle times.
Lower risk of human error and contamination.
Better utilization of fab floor space and resources.
Carriers from Hiner-pack are designed for easy integration. They support advanced automation in diverse fab environments.
Maintenance and Cleaning Protocols
Regular maintenance is vital for wafer carrier performance. Contamination buildup can lead to wafer defects.
Cleaning procedures vary by carrier type and usage. Common methods include ultrasonic cleaning and chemical baths.
Best practices for maintenance:
Inspect carriers periodically for wear or damage.
Clean after each use in critical process steps.
Replace seals and components as recommended by the supplier.
Document cleaning cycles to ensure consistency.
Proper care extends carrier life. It also maintains fab cleanliness standards.
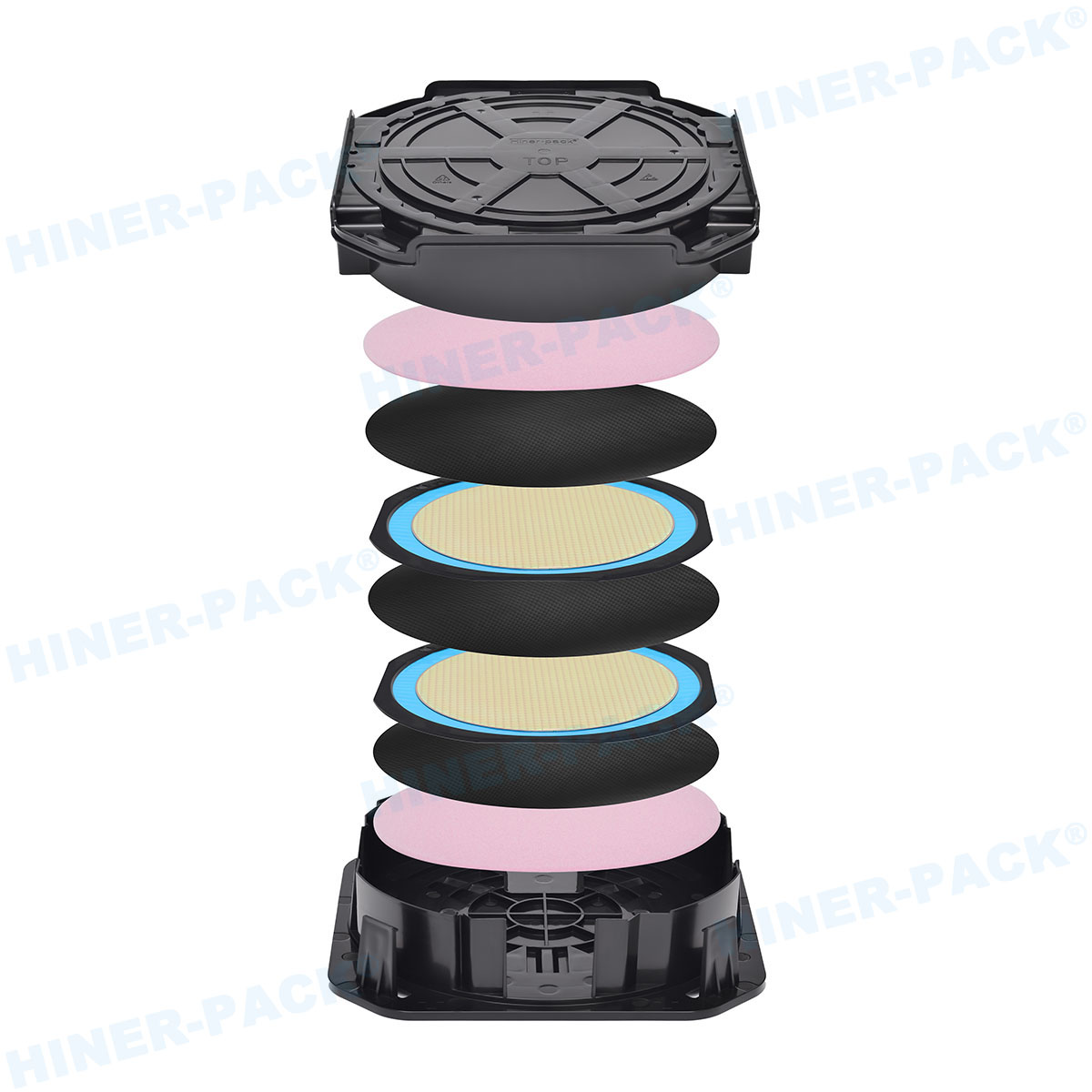

Industry Standards and Compliance
Wafer carriers must adhere to international standards. SEMI standards guide design, testing, and use.
Key standards include SEMI E1.9 for dimensional specs. SEMI E57 covers RFID requirements for tracking.
Compliance ensures:
Interoperability with global fab equipment.
Consistent quality and safety across the supply chain.
Reduced risk of non-conformance in audits.
Suppliers like Hiner-pack certify their carriers to these standards. This reliability is crucial for fab operations.
Selecting a Wafer Carrier Supplier
Choosing the right supplier impacts fab efficiency. Factors include product quality, support, and cost.
Evaluate suppliers based on their industry experience. Look for customization options to meet specific needs.
Considerations for selection:
Product range: Availability of carriers for different wafer sizes.
Technical support: Assistance with integration and troubleshooting.
Lead times and logistics for timely delivery.
Compliance with relevant SEMI and ISO standards.
Hiner-pack offers reliable wafer carrier for fab plant solutions. Their products are tested for durability and cleanliness.
Cost and Return on Investment
Wafer carriers represent a significant investment. However, they contribute to overall fab profitability.
High-quality carriers reduce wafer loss and rework. They also lower maintenance costs over time.
ROI factors include:
Yield improvement from reduced contamination.
Longer carrier lifespan with proper care.
Energy savings from efficient automation compatibility.
Minimized downtime due to carrier failures.
Selecting carriers from trusted brands like Hiner-pack ensures value. It supports sustainable fab operations.
Future Trends in Wafer Carrier Technology
The semiconductor industry evolves rapidly. Wafer carriers are adapting to new challenges.
Trends include smarter carriers with embedded sensors. These monitor conditions like temperature and humidity.
Other developments:
Lightweight materials to reduce handling energy.
Enhanced designs for larger wafer sizes, such as 450mm.
Improved recycling and sustainability practices.
Integration with Industry 4.0 for data analytics.
Staying updated on trends helps fabs remain competitive. A robust wafer carrier for fab plant is key to this progress.
In summary, a wafer carrier for fab plant is fundamental to semiconductor manufacturing. It protects wafers, enables automation, and supports high yields. By understanding types, functions, and selection criteria, fab professionals can optimize their processes. Partnering with suppliers like Hiner-pack ensures access to quality carriers that meet industry demands.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What is the main difference between a FOUP and a FOSB?
A1: A FOUP (Front Opening Unified Pod) is used within a fab for processing wafers, while a FOSB (Front Opening Shipping Box) is designed for shipping wafers between facilities, with added protection for transport.
Q2: How does a wafer carrier prevent contamination in a fab?
A2: Wafer carriers seal wafers in a controlled environment, using materials that minimize particle generation and static discharge. They reduce exposure to airborne contaminants during handling.
Q3: What standards should a wafer carrier comply with?
A3: Wafer carriers should comply with SEMI standards, such as SEMI E1.9 for dimensions and SEMI E57 for RFID. Compliance ensures compatibility and safety in global fabs.
Q4: How often should wafer carriers be replaced?
A4: Replacement depends on usage and wear. With proper maintenance, carriers can last for years. Regular inspection helps identify when replacement is needed to avoid defects.
Q5: Can wafer carriers be customized for specific fab needs?
A5: Yes, many suppliers, including Hiner-pack, offer customization for size, material, and features to match unique fab requirements and processes.
Q6: Why is automation compatibility important in wafer carriers?
A6: Automation compatibility allows carriers to interface with robotic systems, increasing handling speed, reducing manual errors, and improving overall fab efficiency and yield.